How Does Margin in Forex Work?
Margin in forex lets you control larger trades with a smaller deposit, giving you more market exposure without tying up all your capital. Learn how margin, leverage, and risk work together — and how to manage them effectively to trade smarter and stay in control.

Margin trading in forex allows you to open larger positions using a small deposit. This deposit—called margin—is set aside by your forex broker as a form of collateral. By using margin, traders gain greater market exposure without committing the full amount of money upfront.

In this article, we’ll clearly explain how margin works, why it matters, and how to manage it effectively—whether you’re new to forex or looking to sharpen your understanding.
What is a Margin Account?
A margin account allows traders to control larger trades by depositing just a fraction of the full trade value—known as margin—rather than using the entire amount upfront.
For example, if a brokerage firm requires a 5% margin, a trader only needs to deposit $5,000 to control a $100,000 trade. The remaining $95,000 is effectively borrowed from the broker through leverage, allowing the trader to control a large position with a small upfront investment.
While margin increases opportunity, it also increases risk. Losses are based on the full trade size—not just the margin—so effective risk management is essential for protecting your capital and growing sustainably.
Example of Using Margin in a Forex Trade
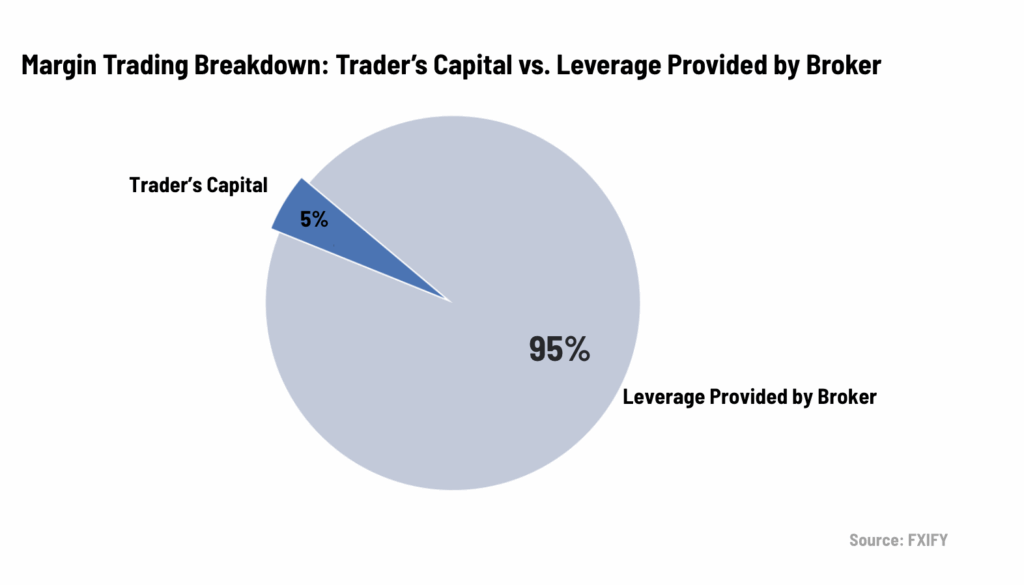
Let’s break down a practical example of margin in forex trading.
Imagine a trader deposits $5,000 into their margin account and wants to open two forex positions totalling $100,000. If the forex broker requires a 5% margin, the trader must set aside 5% of $100,000—which equals $5,000.
This means the trader controls a $100,000 position while only committing $5,000. The remaining $95,000 is provided by the broker through leverage.
Tracking Margin Levels & Avoiding Margin Calls
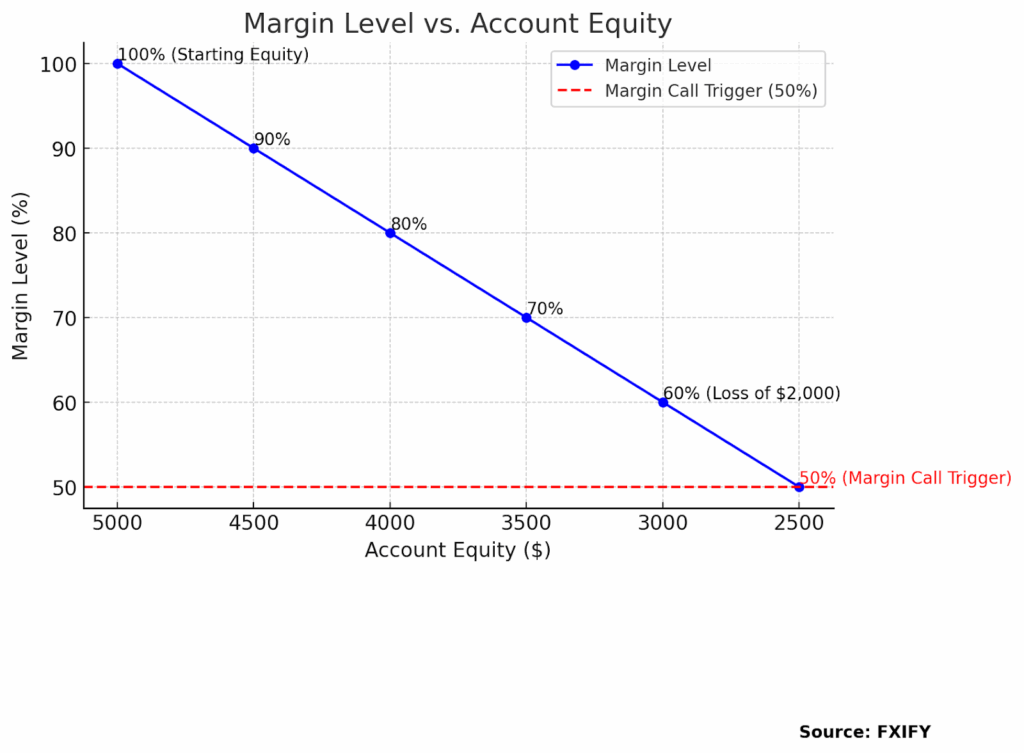
To avoid margin calls, traders must monitor their margin level, which is calculated as:

As shown above, your margin level tells you how much of your margin is backed by your account equity. A level of 100% means you’re fully covered. If it drops to 50% or below, your broker may trigger a margin call.
For example:
- If your account equity is $5,000 and you’re using $5,000 in margin, your margin level is 100%.
- If your equity drops to $3,000, your margin level falls to 60%—getting close to the danger zone.
Leverage vs Margin in For¡ex
You’re probably thinking margin and leverage are the same thing, right?
Not quite. They work together, but they serve different roles in your trading strategy.
| Margin | The capital set aside by the trader to open and maintain a trade. |
| Leverage | The amplified trading power that allows a trader to control a larger position than their deposit. |
How They Work Together
Margin enables leverage by letting traders open positions larger than their initial deposit. The leverage ratio determines how much market exposure they gain based on the margin they commit.
Let’s look at an image that better explains this relationship.
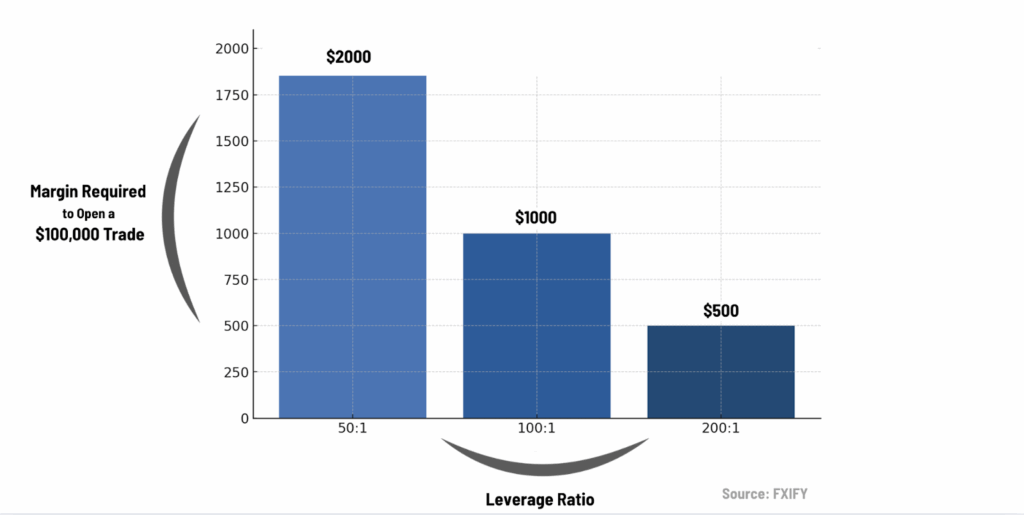
As you can see, the amount of margin required decreases as leverage increases when opening a $100,000 forex position. Higher leverage reduces the upfront capital required, but also increases risk exposure.
For example:
- With 50:1 leverage, a trader needs $2,000 in margin to control a $100,000 position.
- With 100:1, only $1,000 is needed.
- With 200:1, margin drops to just $500.
The amount of margin required can vary by forex broker, depending on their leverage offerings.
| IMPORTANT TO NOTE: Leverage amplifies profits, but also magnifies losses. Since losses are calculated on the full trade value, not just margin, traders can quickly deplete their account if they don’t manage risk properly. |
How to Calculate Forex Margin
Before opening a trade, it’s important to understand how much margin you’ll need. Using a forex margin calculator can help, but knowing the formula behind it gives you more control over your strategy.

For example, if you want to open a $100,000 trade and your broker requires a 2% margin, you’d need:
$100,000 × 0.02 = $2,000 in margin.
$100,000 × 0.02 = $2,000 in margin
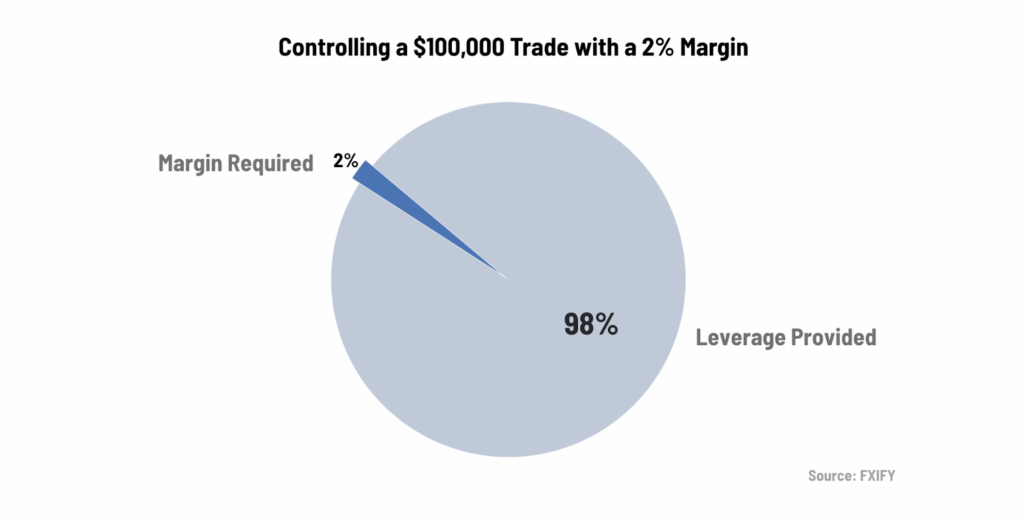
This chart shows how a 2% margin means only $2,000 is required to control a $100,000 trade–the rest is leveraged.
Margin Call Calculation Example
Here’s how a margin call gets triggered when losses reduce account equity below the broker’s required margin level:

In this case, the margin level drops to 40%, triggering a margin call because it’s below the broker’s 50% threshold.
Key Takeaway
Understanding how margin works is essential for managing risk in forex trading. The amount of margin required varies by forex broker and leverage settings, but one thing stays constant: losses are calculated on the full trade size, not just the margin deposit.
By using a margin calculator, tracking your margin level, and setting appropriate stop-losses, you can make informed decisions and avoid unnecessary margin calls. Whether you’re new to forex or scaling up your strategy, mastering margin is key to protecting your capital and trading with confidence.





