What is Leverage in Trading? A Guide for Beginners
Understand how forex leverage works, its pros and cons, and how FXIFY™ helps traders manage risk effectively.

Leverage is a double-edged sword in forex trading, allowing traders to control larger positions with a smaller initial deposit. By using borrowed funds, traders can amplify both potential profits and losses. While this makes leverage attractive, it also comes with substantial risks that require careful management. Therefore, understanding leverage and the risks involved is crucial before diving in.
Forex brokers and prop trading firms, like FXIFY™, offer leverage to traders looking to increase their market exposure with less upfront capital with less upfront capital. This guide will break down the fundamentals of leverage, including leverage ratios, margin requirements, and risk management strategies, helping you make informed decisions in your trading journey.
Leverage Definition
Leverage is a key feature in CFD trading that allows you to gain greater market exposure with a smaller initial investment. It is a financial tool that allows you to open larger trading positions by using a small portion of your own funds (margin), rather than paying the full value of the trade upfront.
In trading, leverage is expressed as a ratio, e.g.,30:1, meaning you can control a position that is 30 times larger than your trading capital.
A key concept in leverage is margin – the amount of capital you must deposit to open and maintain a leveraged position. Leverage makes forex trading more accessible, but you must learn to use it wisely to manage risk effectively.
How Leverage Works
Before diving into how leverage works, remember that ‘margin’ refers to the funds you deposit as a security for opening and maintaining your trading positions. Since most brokers and prop firms operate on a margin-based leverage system, understanding this concept is crucial for effective risk management.
Example: The Impact of Leverage on Trading
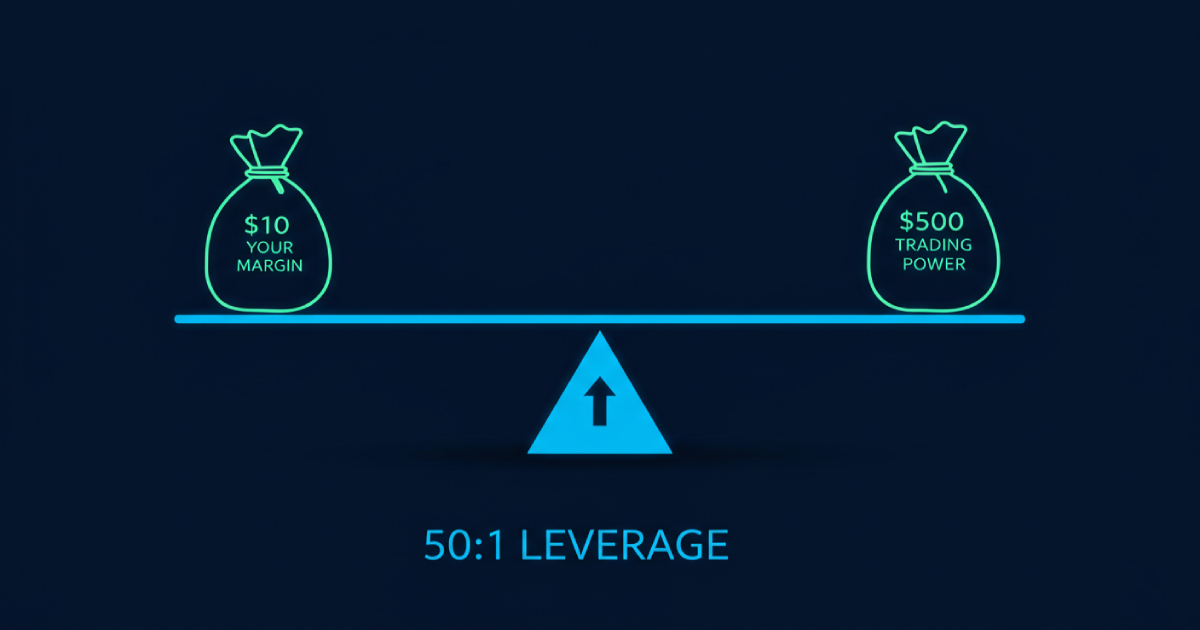
Let’s say you open a forex trading account with $10 and use 50:1 leverage. This means your trading capital effectively becomes $500. If the exchange rate moves in your favour, your profits are amplified. However, the same applies to losses; just a small market fluctuation could wipe out your account.
Understanding Margin Terms Related to Leverage
In forex trading, several key margin terms are essential to grasp:
- Initial Margin: This is the minimum margin requirement—or good faith deposit—needed to open a new position.
- Used Margin: The portion of your account balance currently allocated to maintain open positions.
- Free Margin: Also known as usable margin, this is the equity in your account that is not tied up in open positions and can be used to open additional trades.
- Equity: The total value of your trading account, calculated by adding your account balance to any unrealised profits or losses. Equity serves as the foundation for determining your free margin and margin level.
- Margin Level: Expressed as a percentage, it is calculated by dividing your equity by the used margin and multiplying by 100. It indicates the health of your trading account.
- Margin Call: A notification that your margin level has fallen below a predefined threshold set by your broker (e.g.,100% or 50%), prompting you to deposit additional funds or close positions to maintain your open trades.
- Liquidation: If your account equity falls below the maintenance margin requirement, your broker may automatically close your positions to prevent further losses.
Balancing Opportunity and Risk Management
While leverage offers the opportunity to enhance profits, it equally increases the potential for substantial losses. Effective risk management strategies are vital when trading with leverage. This includes setting appropriate stop-loss orders, monitoring your margin levels, and avoiding over-leveraging your account. Traders should always monitor their margin levels and ensure they have enough remaining funds to avoid unexpected liquidation of positions.
Visualising the Relationship Between Margin Terms
To better understand how these margin terms interact, consider the following diagram:
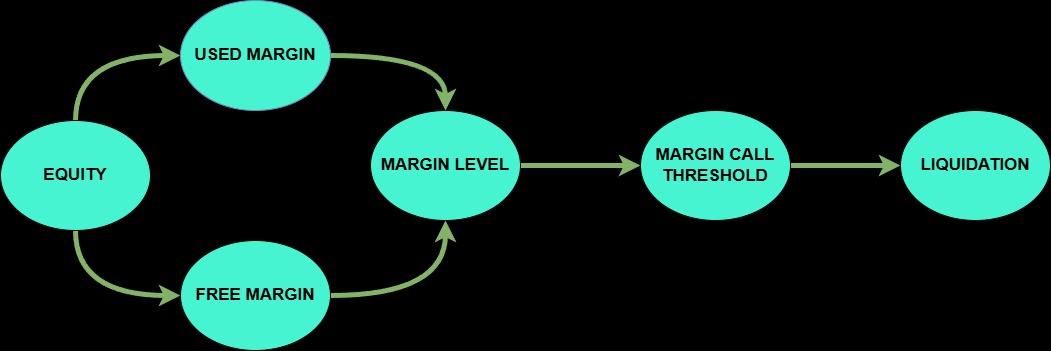
In this diagram, your equity is divided into used margin and free margin. The margin level is continuously monitored to stay above the margin call threshold (e.g., 100% or 50%). If it falls below this level, a margin call is issued, and if not addressed, it can lead to position liquidation.
Leverage Trading Benefits
Leverage enables traders to participate in the forex market with a lower initial deposit, unlocking more trading opportunities. With leverage, you can more easily diversify into different trades and markets like metals and stock CFDs without needing the full trade value upfront. Each market has its leverage preset, allowing traders to optimise their positions based on risk tolerance and capital availability.
At FXIFY, we offer competitive leverage tailored to different account plans and asset classes, as detailed in the following tables:
| Instrument | Standard Leverage | Maximum Leverage (with Add-on) |
| Forex & Gold | 30:1 | 50:1 |
| Indices | 10:1 | N/A |
| Stocks & Cryptocurrencies | 2:1 | N/A |
Standard Account Leverage
| Instrument | Leverage |
|---|---|
| FX & Gold | 30:1 (Up to 50:1) |
| Indices | 10:1 |
| Oil | 5:1 |
| Stocks | 2:1 |
| Crypto | 2:1 |
Instant Funding Account Leverage
| Instrument | Leverage |
|---|---|
| FX | 50:1 |
| Commodities | 20:1 |
| Indices | 15:1 |
| Oil | 20:1 |
| Crypto | 2:1 |
| Stocks | 2:1 |
Lightning Plan Leverage
| Instrument | Leverage |
|---|---|
| FX & Gold | 30:1 (Up to 50:1) |
| Indices | 10:1 |
| Oil | 5:1 |
| Stocks | 2:1 |
| Crypto | 2:1 |
Potential for Higher Profits
Higher leverage ratios allow for magnified profits, but also at the risk of bigger losses. By using good risk management, leverage can be a powerful tool, allowing even modest market movements to result in significant returns. This means you can maximise your earning potential and explore more diverse trading strategies, all while using only a fraction of the account balance as used margin.
Trade Management
Effective trade management is essential when using leverage, as it allows traders to maximise opportunities while managing risk. Moreover, many brokers and prop trading firms enable you to diversify across multiple currency pairs to spread and manage risk more effectively.
Can You Trade Without Leverage?
Yes, you can. Indeed, some brokers may offer leverage options such as 1:1.
In these scenarios, traders utilise only their capital to take positions at the current market price, rather than borrowing funds to control a larger trade size. As a result, you would need significantly more capital to achieve the same level of market exposure that leverage would allow.
Trading without leverage eliminates the complexities of leverage calculations and reduces the risk associated with excessive leverage. It is a more conservative approach to managing your trading account and aligns with sound risk management principles crucial for success in prop trading firms.
This approach is similar to stock trading in some ways. While traditional stock purchases often involve paying the full price upfront, leverage is also available in stock trading, though it usually involves borrowing funds through margin accounts. Stock leverage is more literal and heavily regulated, with lower leverage limits compared to forex or CFDs. In non-leveraged stock trades, your entire deposit covers the full value of the position, and any gains or losses are realised at 1:1 exposure.
Alternatively, some traders choose to use lower leverage as a deliberate risk management strategy, accepting potentially smaller gains in exchange for a more stable, predictable trading experience.
Managing Risk When Trading with Leverage

While leverage increases potential rewards, it can also put a trader’s position at excessive risk of being liquidated. Successful traders prioritise risk management to protect their capital and avoid unnecessary exposure.
Choosing the Right Leverage for Your Account
When opening an account, you can set limits on your leverage to manage risk effectively. Lower leverage (e.g., 10:1 or 30:1) minimises exposure to market fluctuations, while higher leverage (e.g., 50:1 or more) amplifies both potential gains and losses. Be sure to choose a leverage ratio that aligns with your risk tolerance and trading strategy.
Proper Position Sizing
Properly sizing your trading positions is critical. The ideal position size should align with your overall strategy and be proportionate to your total account balance, ensuring that the margin required for each trade does not expose you to undue risk.
One way to estimate position size is:
| Risk Per Trade (%) = (Account Balance × Risk Percentage) ÷ (Stop-Loss Distance in Pips × Pip Value) |
For instance, if a trader has a $10,000 account and risks 1% per trade, they might cap their potential loss at $100 per position.
Risk-to-Reward Ratios
Risk-to-reward ratios often guide decision-making in leveraged trading. Many traders aim for a minimum 1:2 risk-to-reward ratio, meaning that for every $1 risked, the potential return is $2.
Using Stop-Loss Orders
Stop-loss orders act as a safety net. They serve as price alerts to exit trades before significant losses occur, automatically closing your position when the price reaches a predetermined level. Using stop-loss orders is a crucial risk management tool in preventing further losses.
Trading Strategy & Margin Considerations
When developing your trading strategy, be sure to consider current margin rates across different asset classes. Ensuring that the margin required for each trade aligns with your risk management approach is crucial for long-term success—especially when trading with higher leverage.
Technical analysis like RSI divergence can help with exit points but should be part of a broader risk-adjusted approach. And understanding how real leverage affects your position is key as misusing it can be risky while disciplined management can be very profitable over time.
FXIFY Leverage
Many prop firms, including FXIFY™, provide flexible leverage options to cater to different trading strategies. Standard accounts offer 30:1 leverage, providing a balance between risk and reward. Forex traders should carefully consider how much leverage they are comfortable with.
For traders seeking higher leverage, FXIFY offers the option to upgrade to 50:1 leverage via the ‘Increase Leverage’ add-on at checkout. These options allow for leveraged forex trading on instruments such as Forex & Gold, Indices, and Stocks & Cryptocurrencies through a user-friendly trading platform.
FAQs: Your Leverage Questions Answered
What does 500:1 leverage mean?
It means you control $500 for every $1 in your account. If you deposit $100, you can trade up to $50,000.
How much is $100 with 10x leverage?
With 10:1 leverage, your $100 gives you a trading power of $1,000.
Do you pay back leverage?
Leverage in forex trading is not a loan but a trading mechanism. However, if your losses exceed your margin, you may face a margin call requiring additional funds.
Is leverage good for beginners?
While leverage in forex trading can boost profit potential, it is extremely risky for inexperienced traders. Beginners are advised to avoid high leverage to reduce exposure to sudden market downturns and should start with lower leverage ratios (e.g., 10:1). Be sure to use risk management tools like stop-loss orders to avoid margin calls triggered by volatile market prices.
What leverage is good for beginners?
Lower leverage (10:1 or 30:1) is recommended to minimise risk.





