Fair Value Gap Strategy: Spot & Trade Profitable Gaps
Unlock the power of Fair Value Gaps (FVGs) in your trading. Learn how to identify, trade, and combine them with Smart Money Concepts for better decision-making.

Fair Value Gaps (FVGs) are a favourite tool among traders who use Smart Money Concepts (SMC) to identify potential opportunities in the market.
An FVG occurs when price moves quickly, leaving a gap in the chart that can signal where the market might return to before continuing its trend. This offers traders valuable insight into price retracements or continuations.
In this guide, we’ll explore how to spot these gaps, the different types of FVGs, and strategies to trade them effectively.
What is a Fair Value Gap?
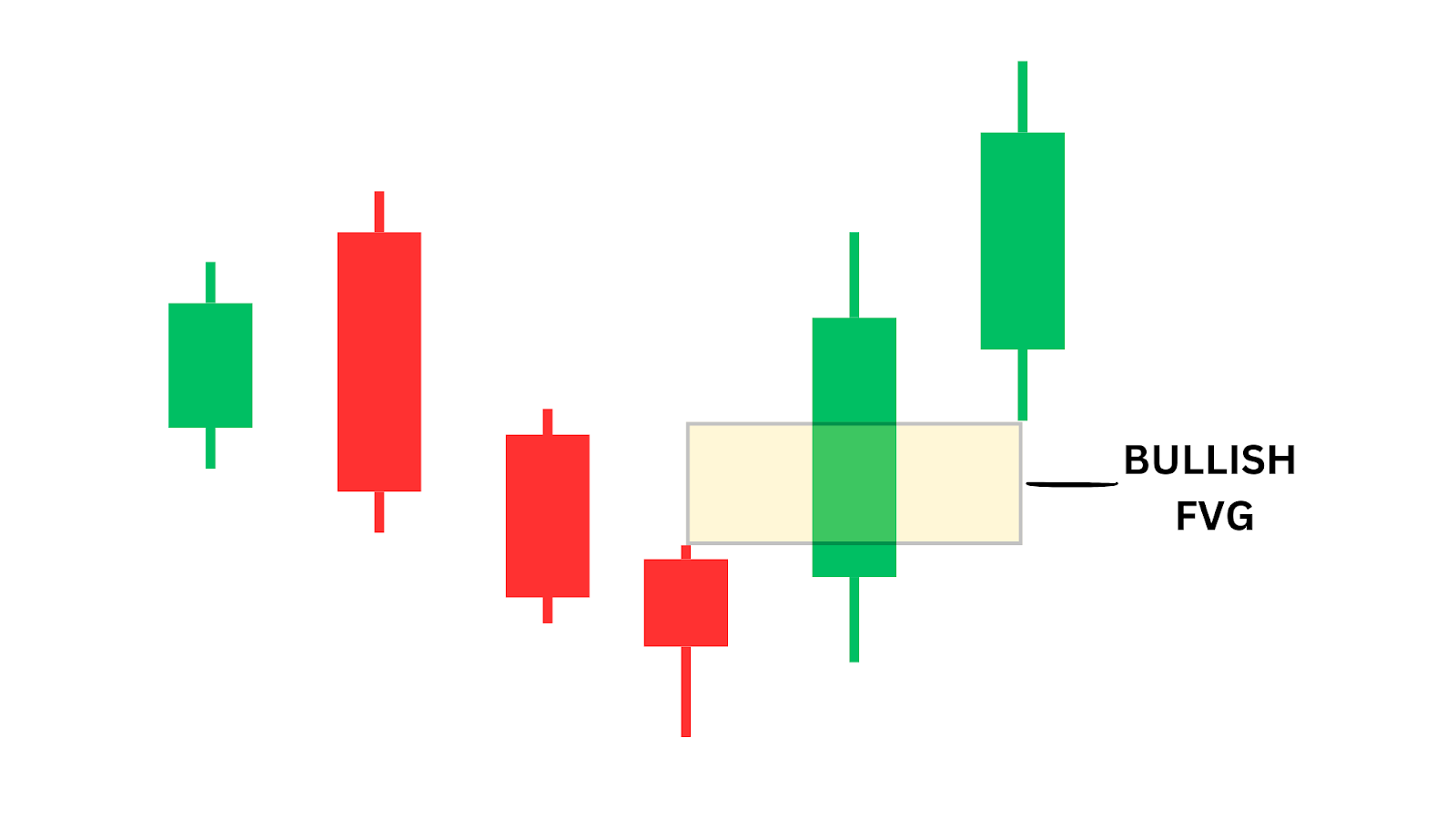
A Fair Value Gap occurs when there is an imbalance in the market between buyers and sellers, resulting in a gap between price candles.
The gap is defined by the space between three candles, where the middle candle has a solid area which has no overlap with the wicks of candles before and after it.
This gap typically appears on the chart when the price moves impulsively, creating a powerful move in a single direction. These gaps act as zones where price is likely to revisit before continuing its movement, providing excellent entry opportunities for traders.
Fair Value Gaps can serve as strong support or resistance levels depending on their location:
- FVGs below the current price are bullish fair value gaps, acting as support.
- FVGs above the current price are bearish fair value gaps, acting as resistance.
Types of Fair Value Gap Formations
Fair Value Gaps can appear in various forms and timeframes. Here are a few key things to remember:
- Timeframes: FVGs can appear in any timeframe, from 1-minute charts to weekly charts. It’s important to look for confluence with higher timeframes for more reliable setups.
- Position of Price: Whether the price is above or below the FVG impacts how you should trade it. A successful retest of the FVG may provide a great entry point.
- Tapped vs. Untapped: Tapped FVGs are less powerful than untapped ones. A stronger FVG will be one that the price hasn’t revisited yet.
Examples of Fair Value Gaps
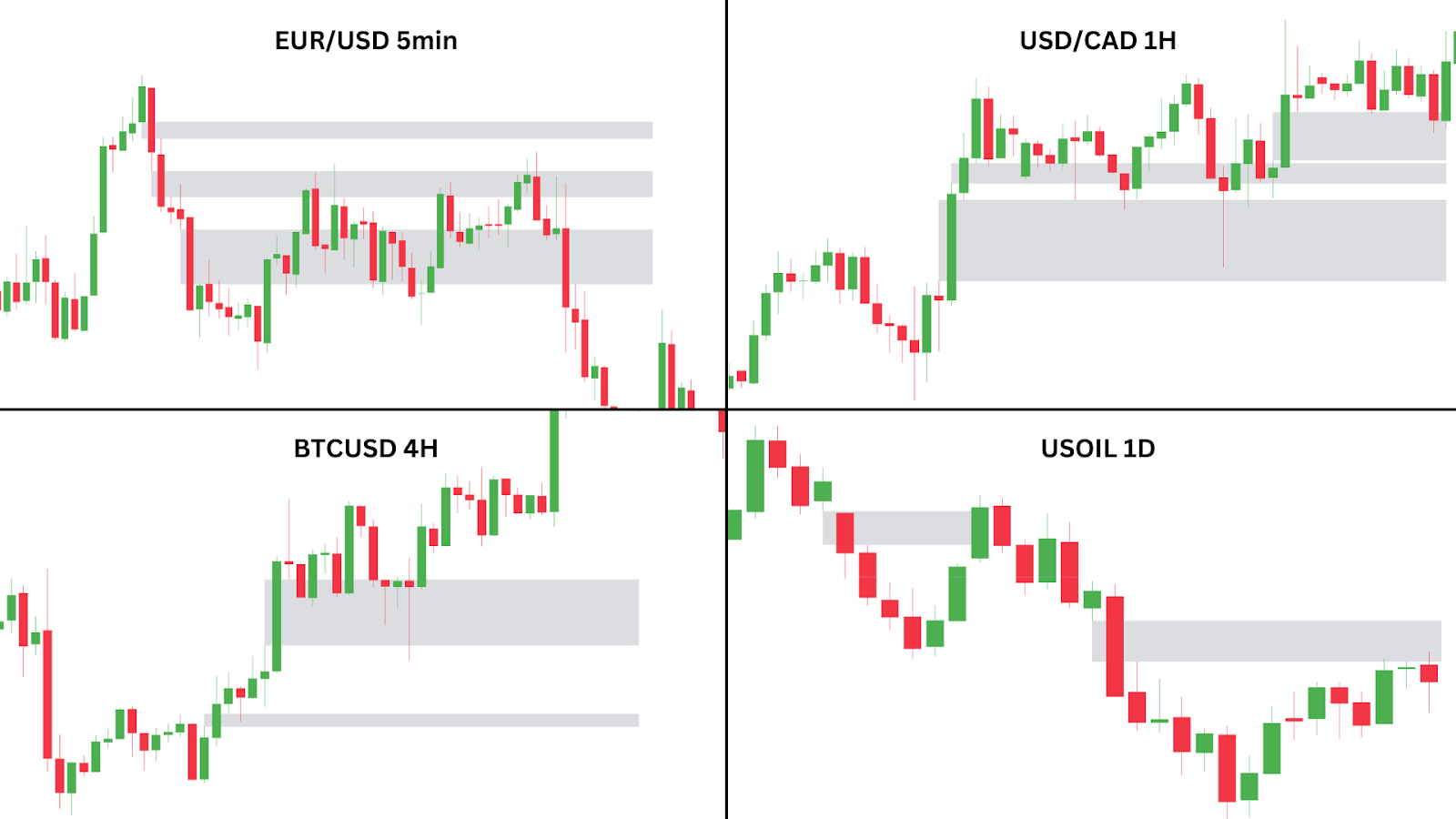
In practice, Fair Value Gaps (FVGs) are highly common, appearing across all timeframes and markets. They can be spotted on Forex charts, Stocks, Bitcoin, and various other markets on the 5 minute timeframe, to the daily or even monthly timeframes.
For example, take a look at the four charts displayed above:
| On the EUR/USD 5-minute chart: Notice how there can be more than one FVG formed in succession. Additionally, not all gaps lead to significant price reactions. Some are respected, while others are ignored. This highlights the importance of combining FVGs with additional tools, like Order Blocks or market structure changes, which can help traders identify the more reliable gap to trade. |
| On the USD/CAD 1-hour chart: Bullish FVGs have formed below the current price, indicating potential zones of support. These gaps suggest areas where price may reverse to the upside as it pulls back, offering clues for bullish price movements in the same direction of the prevailing trend. |
| On the BTC/USD 4-hour chart: We see two FVGs that indicate potential zones for price retracement. The closest FVG provided a strong bounce, leaving the lowest FVG untouched. If combined with other Smart Money Concepts (SMC) like Order Blocks, we can see the reason for this – the closest FVG is in-line with a formation of the bullish order block. We will get into this in more detail later. |
| Finally, on the USOIL (WTI) Daily chart: We see two bearish FVGs that act as overhead resistance. These suggest where the USOIL price might face resistance in the event the price moves higher. Keeping track of these FVGs is key to finding potential short setups. |
Case Study: EUR/USD, 5min Fair Value Gap
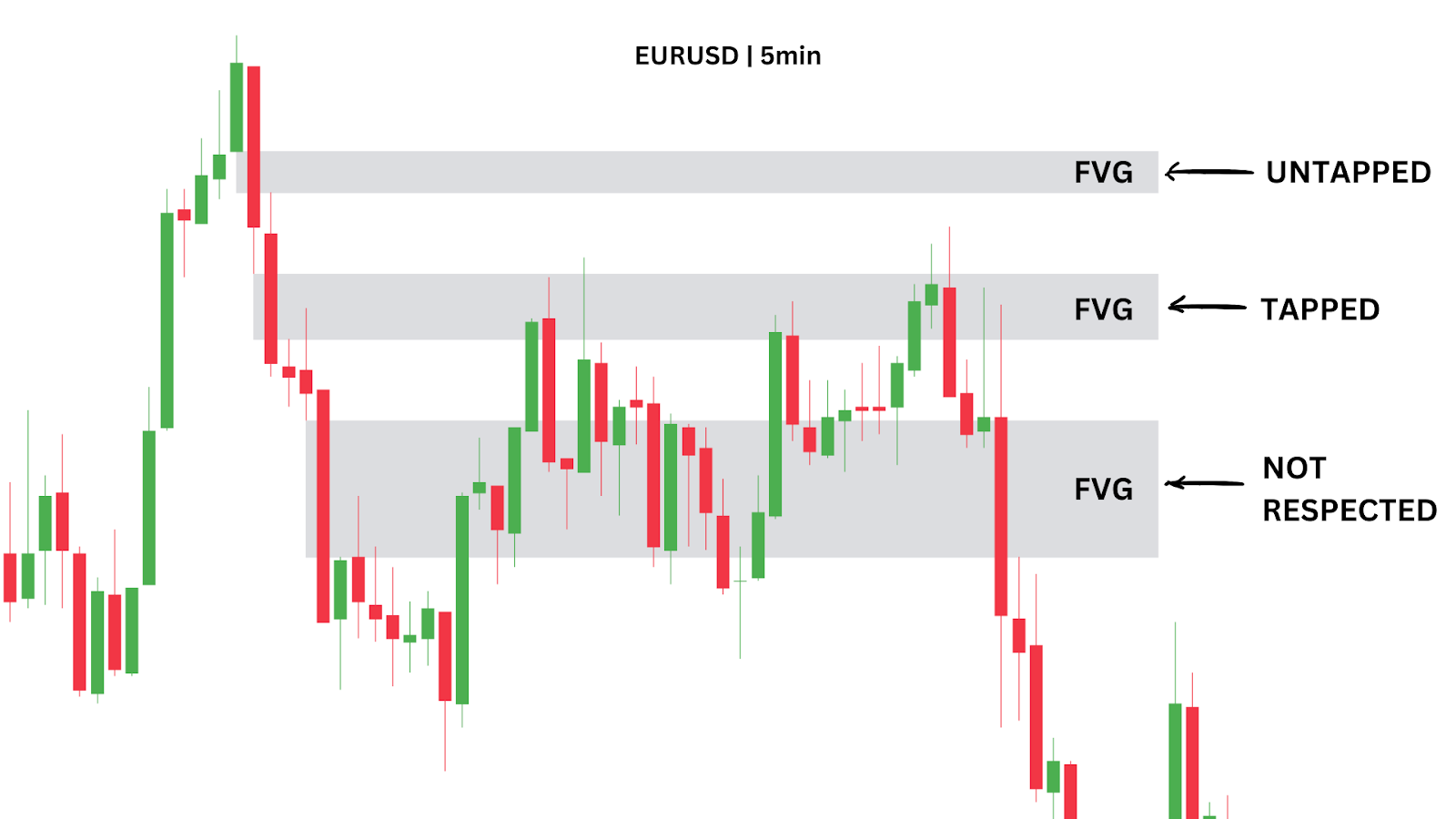
In this EUR/USD 5-minute chart, we observe a strong upward price movement followed by a sharp reversal. This creates several bearish Fair Value Gaps (FVGs) on the way down. These gaps suggest potential areas where the market sentiment is likely to retrace before continuing its bearish move.
However, not every FVG is a solid trade opportunity. It’s essential to combine FVGs with other Smart Money Concepts like the Change of Character (ChoCh), Order Blocks, or even traditional tools like Fibonacci retracement to identify the most reliable entry points.
For example, the top FVG in this chart wasn’t retested by price, and the bottom FVG was traded through without holding. Both would have been weak trade opportunities. But stick around – in method three we’ll explain how the Fibonacci tool could have guided you to ignore these and instead enter a trade at the middle FVG, which provided a near-perfect entry point.
How to Trade Fair Value Gaps
In trading, adaptability is essential. Fair Value Gaps (FVGs) can be leveraged in various ways, depending on your strategy.
Here are three effective methods to help you identify fair value gaps and integrate them into your trading approach, whether you’re a beginner or refining your strategy.
Method One: Classic FVG Strategy
This strategy focuses on entering a trade after a Fair Value Gap (FVG) forms at a significant support or resistance level, offering a straightforward way to capitalise on price movement.
Wait for an FVG to form on your selected timeframe. Ideally, it should be near a key zone, such as support or resistance, where you expect the price to reverse.
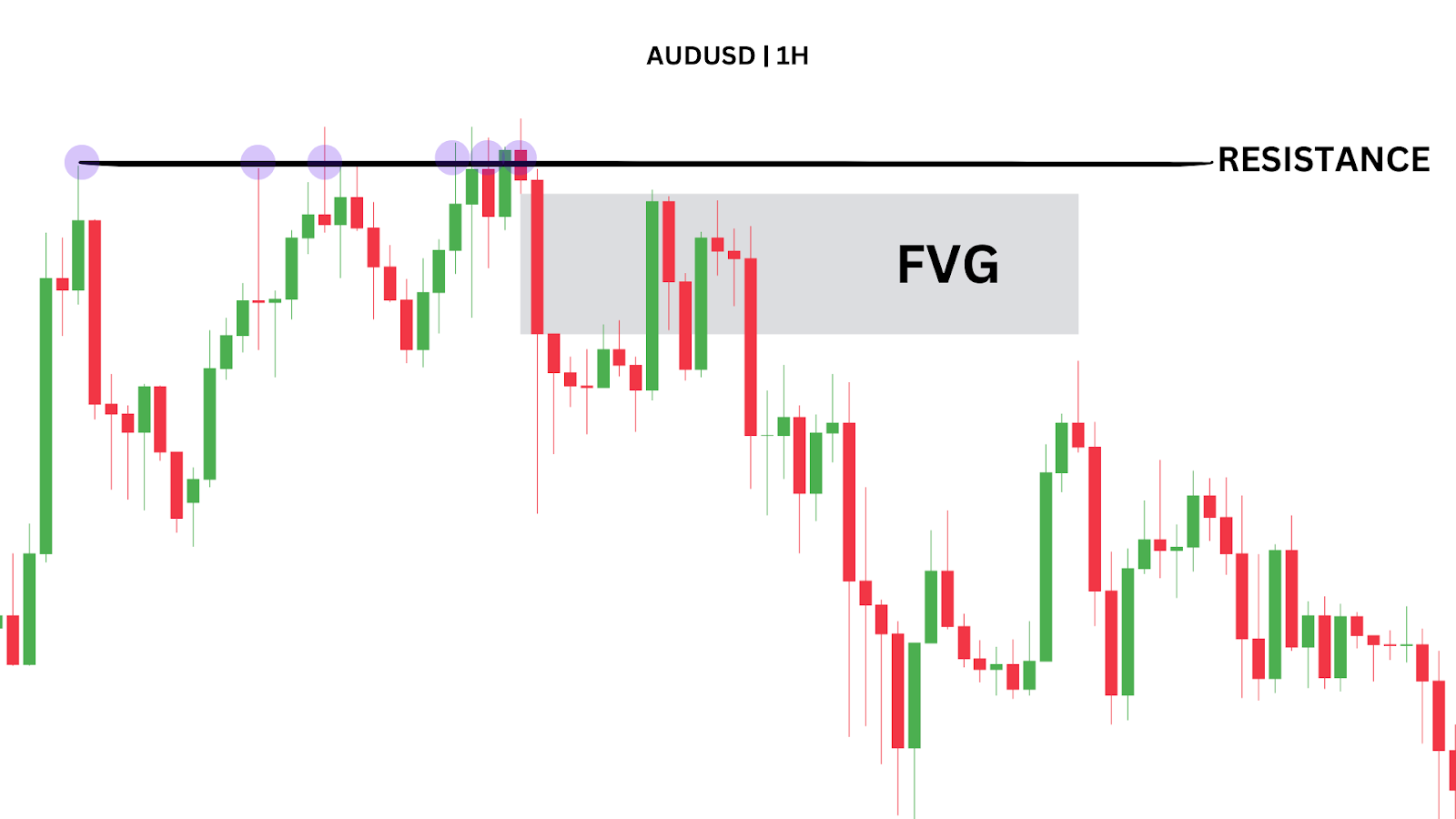
In the AUDUSD 1H example above, price tests a resistance level several times before breaking away, leaving a clean FVG, which provides a clear entry point.
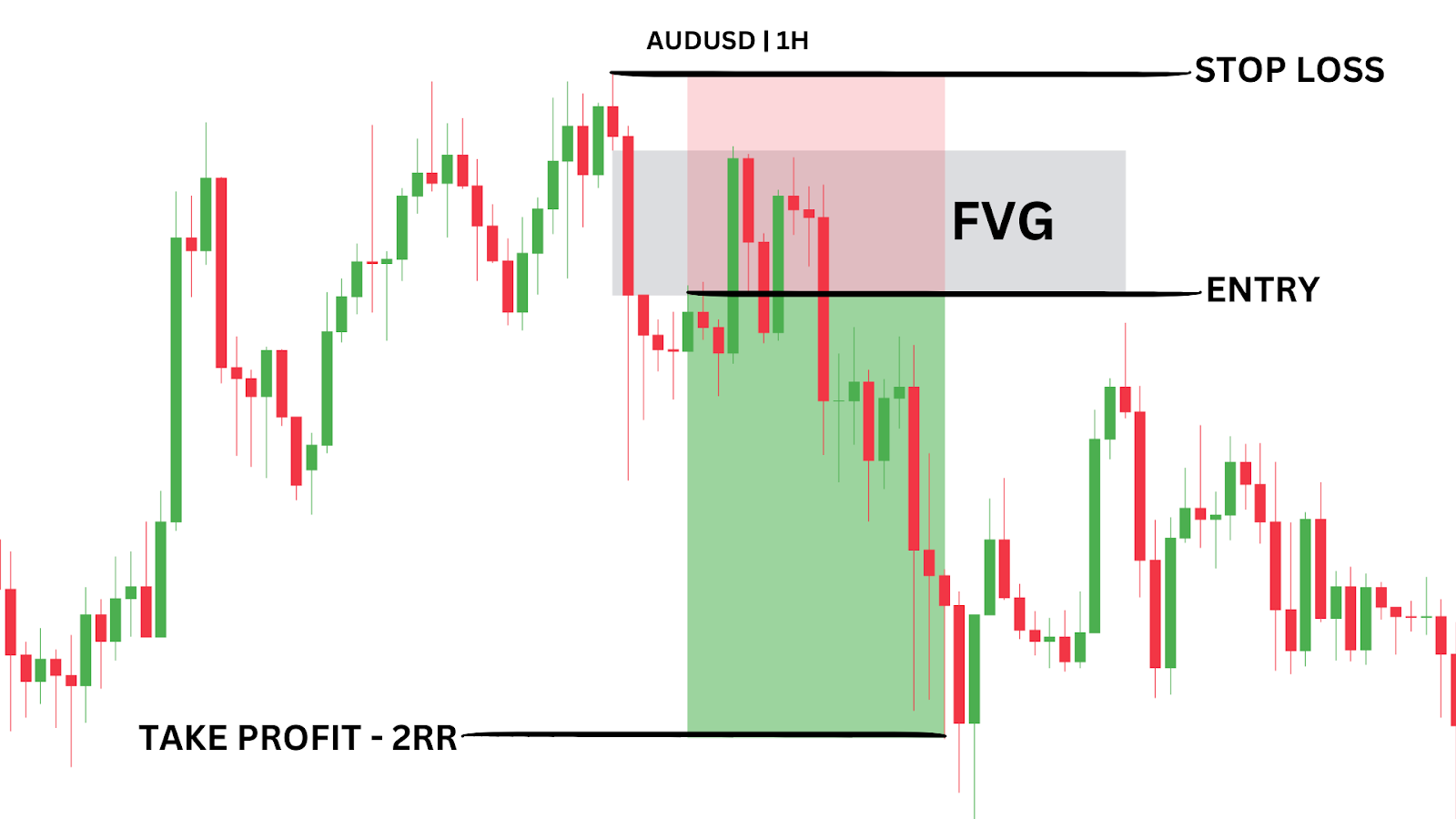
Enter at the FVG, set your stops below the candle that forms the FVG, and aim for a fixed 1:2 risk-to-reward ratio for a simple approach.
Trading Strategy Summary
Entry Point: Enter when the FVG forms at a key support or resistance zone.
Stop-Loss: Place stop-loss below the high/low of the candle forming the FVG.
Profit Target: Target a fixed 1:2 risk-to-reward ratio (2RR).
| PROS: Simple to execute, ideal for beginners, uses straightforward risk management. |
| CONS: May not capture more precise entries, lacks flexibility for more advanced setups, may have increased losses in trending markets. |
Method Two: FVG with Order Block Strategy
This strategy blends Fair Value Gaps with Order Blocks to improve the accuracy of your trade entries. It focuses on spotting areas where big players like banks place orders, which create strong zones for price reversals within Fair Value Gaps, making it easier to find the best entry points.
An order block is a zone where large institutional trades (buy or sell orders) have taken place, creating a key area of support or resistance.
Let’s take a look at XAUUSD on the 4-hour chart.
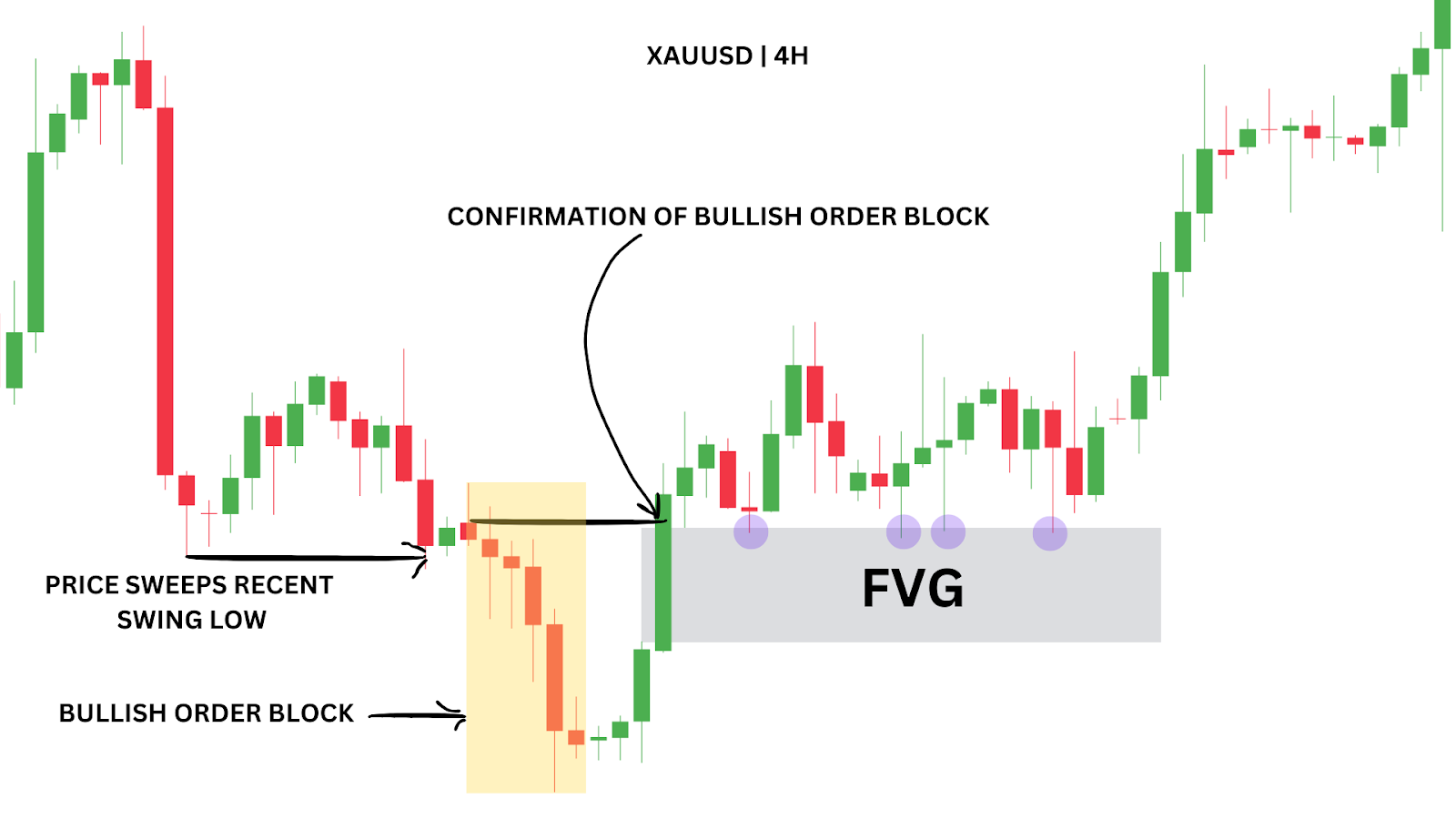
After sweeping a recent swing low, we see a bullish order block (OB) begin to form.
An order block (a bullish order block) is confirmed when a bullish candle closes above the first candle’s open in the block, often forming a strong support level where price is likely to react positively upon revisiting the zone. We can see this above labelled “CONFIRMATION OF BULLISH ORDER BLOCK.”
This particular bullish OB forms as market price pushes upward after sweeping liquidity, with a confirmation candle closing above the OB’s opening price.
Within the confirmation candle, we also see a bullish Fair Value Gap (FVG). This creates a high-probability entry zone where we can set a limit order.
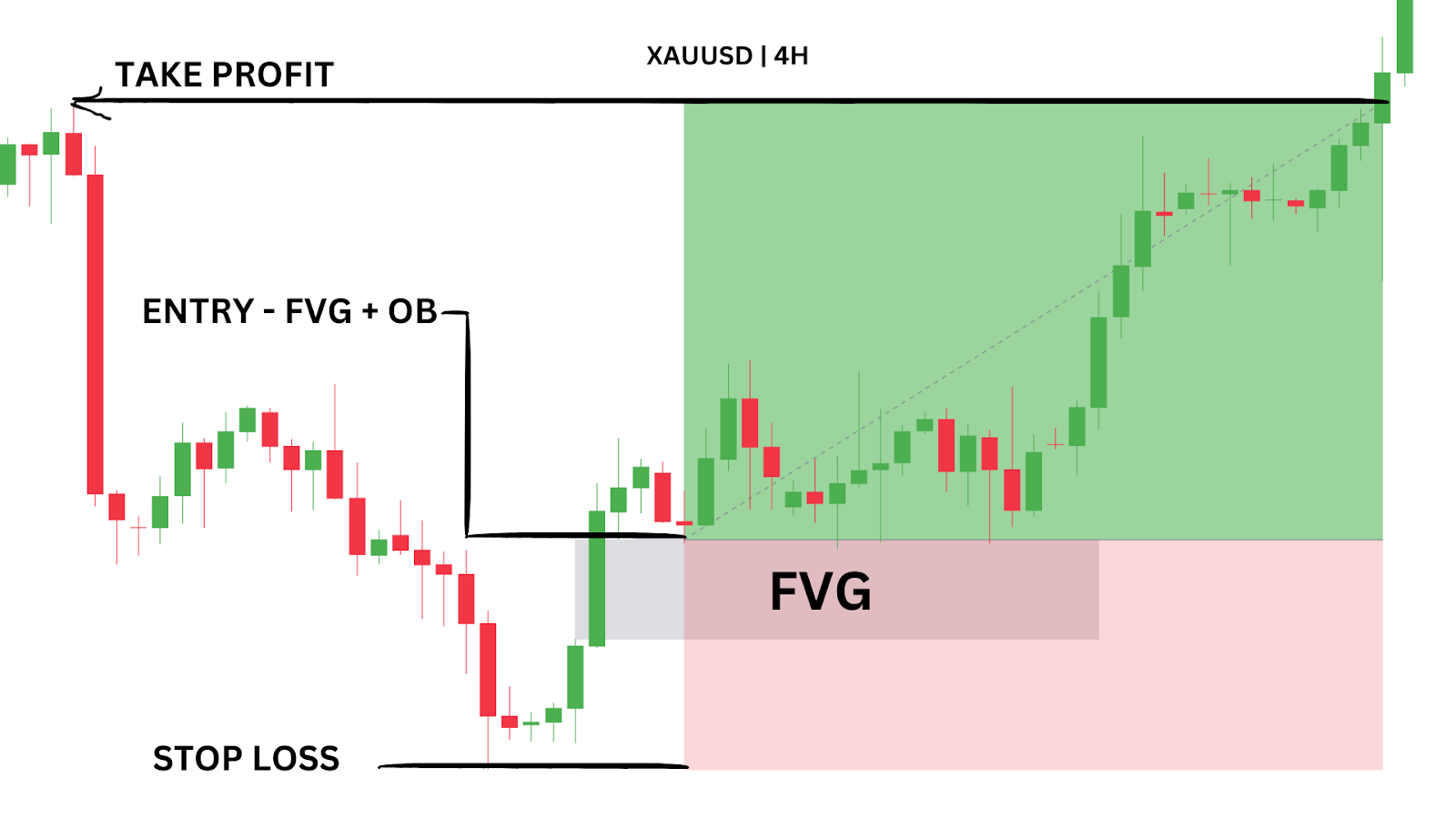
By entering the trade at the FVG, setting our stop-loss below the order block, and targeting the recent pivot high, we can lock in a strong 1.9RR trade with minimal drawdown.
Trading Strategy Summary
Entry Point: Limit entry in the FVG inside the confirmed order block.
Stop-Loss: Set just below the low of the order block.
Profit Target: Recent pivot high, which provides a 1.9 risk-to-reward ratio.
| PROS: Combines two powerful SMC concepts, precise entry points with minimal drawdown, reliable for catching significant reversals. |
| CONS: Requires patience for confirmation, might miss trades if the price doesn’t retest the FVG. |
Method Three: Fair Value Gap Trading with Fibonacci Retracement
This strategy combines Fair Value Gaps with Fibonacci retracement levels to pinpoint high-probability trade entries by aligning the FVG with the 0.618 Fibonacci level for optimal entry.
Let’s bring this back to our EUR/USD 5-minute chart example.
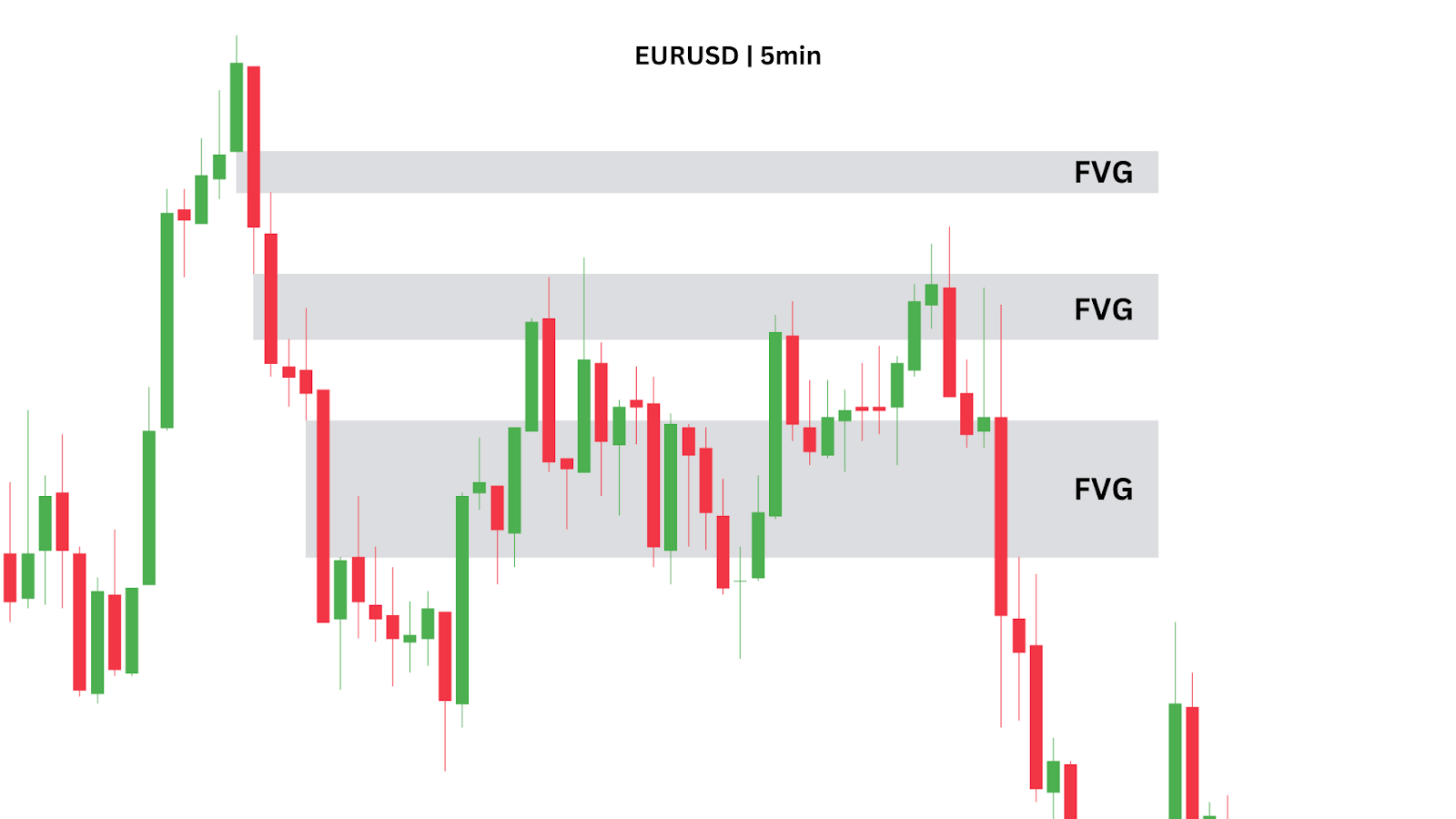
We observe three Fair Value Gaps (FVGs) forming, but which one offers the best trading opportunity?
The top FVG doesn’t get hit, and the bottom one gets traded through, leaving us with the middle FVG as the ideal entry point.
By using the Fibonacci retracement tool, we see that this middle FVG lines up perfectly with the 0.618 retracement level. This adds confluence to the trade setup and helps us choose the correct FVG to trade from. This is how combining well-known technical analysis tools like fibonacci retracements and newer concepts such as FVGs can work to your advantage.
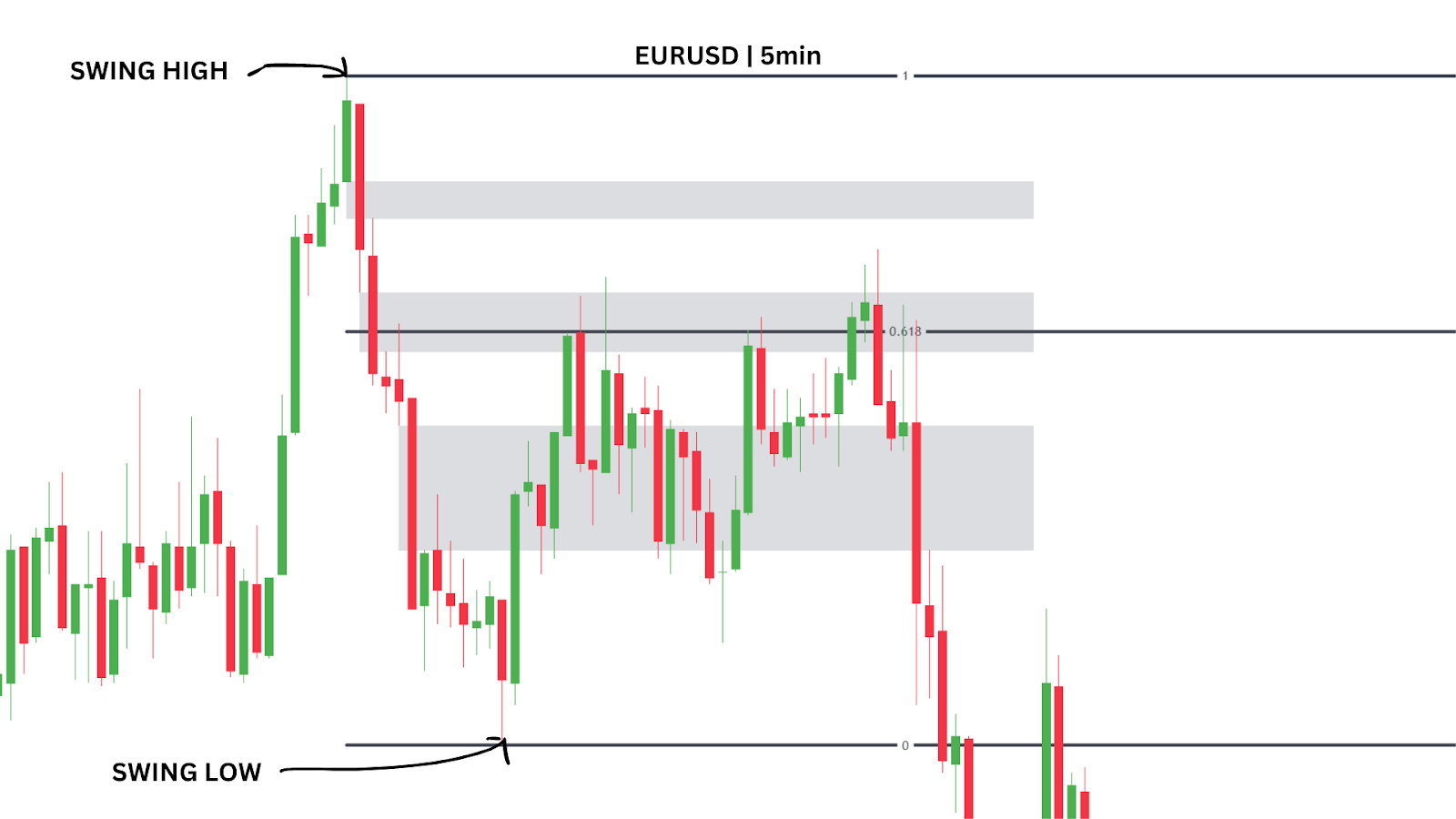
You would draw your Fibonacci from the new confirmed swing low to the most recent swing high. As soon as the price reaches the 0.618 level and taps into the FVG, you can enter the trade.
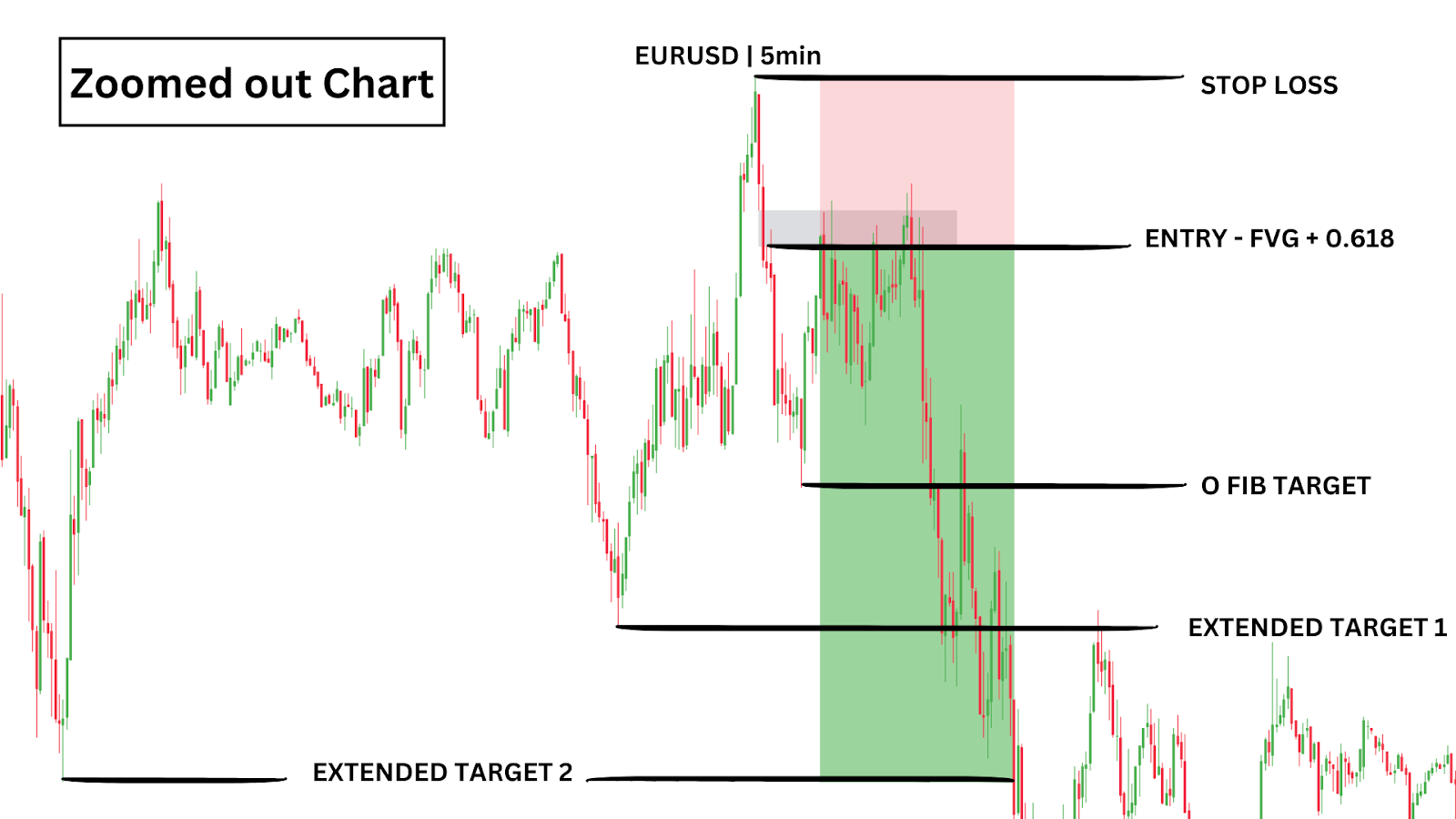
For risk management, place your stop-loss just above the swing high (at the top of the Fibonacci tool) and target the most recent swing low for profit, adjusting based on your risk tolerance:
- First Target: 1.45 Risk-to-Reward (RR) ratio – 0 point in the Fibonacci
- Extended Target 1: 2.25 RR
- Extended Target 2: 3.15 RR
Trading Strategy Summary
Entry Point: Enter at the 0.618 Fibonacci retracement level when it aligns with a FVG, after confirming a new swing low.
Stop-Loss: Place stop-loss just above the swing high.
Profit Target: Target recent swing lows and adjust depending on your risk tolerance (in this case, 1.45RR, 2.25RR, or 3.15RR).
| PROS: Combines two effective trading tools, offers precise entry points, provides strong confluence for high-probability setups, improves risk management by aligning with Fibonacci levels. |
| CONS: Requires patience for confirmations, can result in missed opportunities, more complex for beginners due to multiple analysis layers needed, may be challenging to execute without practice. |
Fair Value Gap Trading vs. Regular Market Gaps
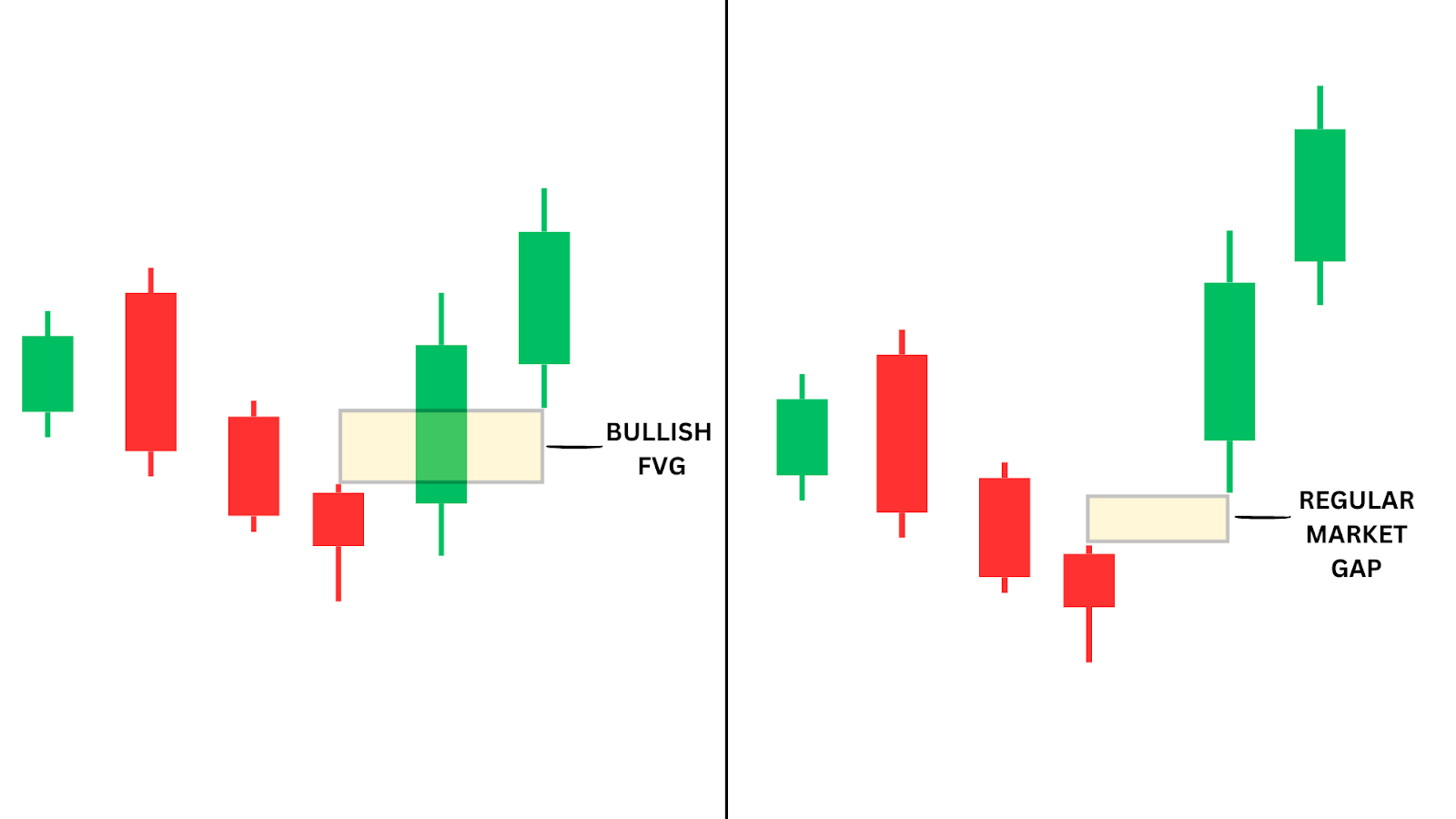
Fair Value Gaps (FVGs) and regular market gaps both show price gaps on a chart, but they differ in their formation and purpose. Market gaps usually occur after major news events or during the opening of trading sessions, where price jumps due to market volatility, leaving a visible “gap” on the chart. These gaps can be influenced by lack of liquidity during non-trading hours.
On the other hand, Fair Value Gaps occur within trading sessions and are caused by rapid price movements that leave a portion of the price action untested. While market gaps leave a clear space between candles, FVGs occur between three candles, where price fails to overlap, indicating buyer-seller imbalances. Traders use FVGs for retracements, while regular gaps are more tied to volatility after major events.
Common Mistakes in Fair Value Gap Trading
- Relying Solely on FVGs: A common mistake is focusing only on FVGs without considering other technical analysis tools. An FVG alone may not provide enough confluence for a successful trade. It’s essential to combine FVGs with other concepts, such as Order Blocks or Fibonacci Retracement, to increase trade probabilities.
- Ignoring Timeframes: Traders sometimes make the mistake of not considering the appropriate timeframe. FVGs may appear strong on lower timeframes but are often less reliable when compared to higher timeframe analysis. It’s important to align FVGs with higher timeframes for better accuracy.
- Overtrading FVGs: Jumping into every FVG setup can lead to overtrading. Not all FVGs are created equal, and some may be invalidated as price continues in a strong trend. Always wait for proper confirmation before entering.
What other SMC Concepts Work Well with Fair Value Gaps?
Order Blocks
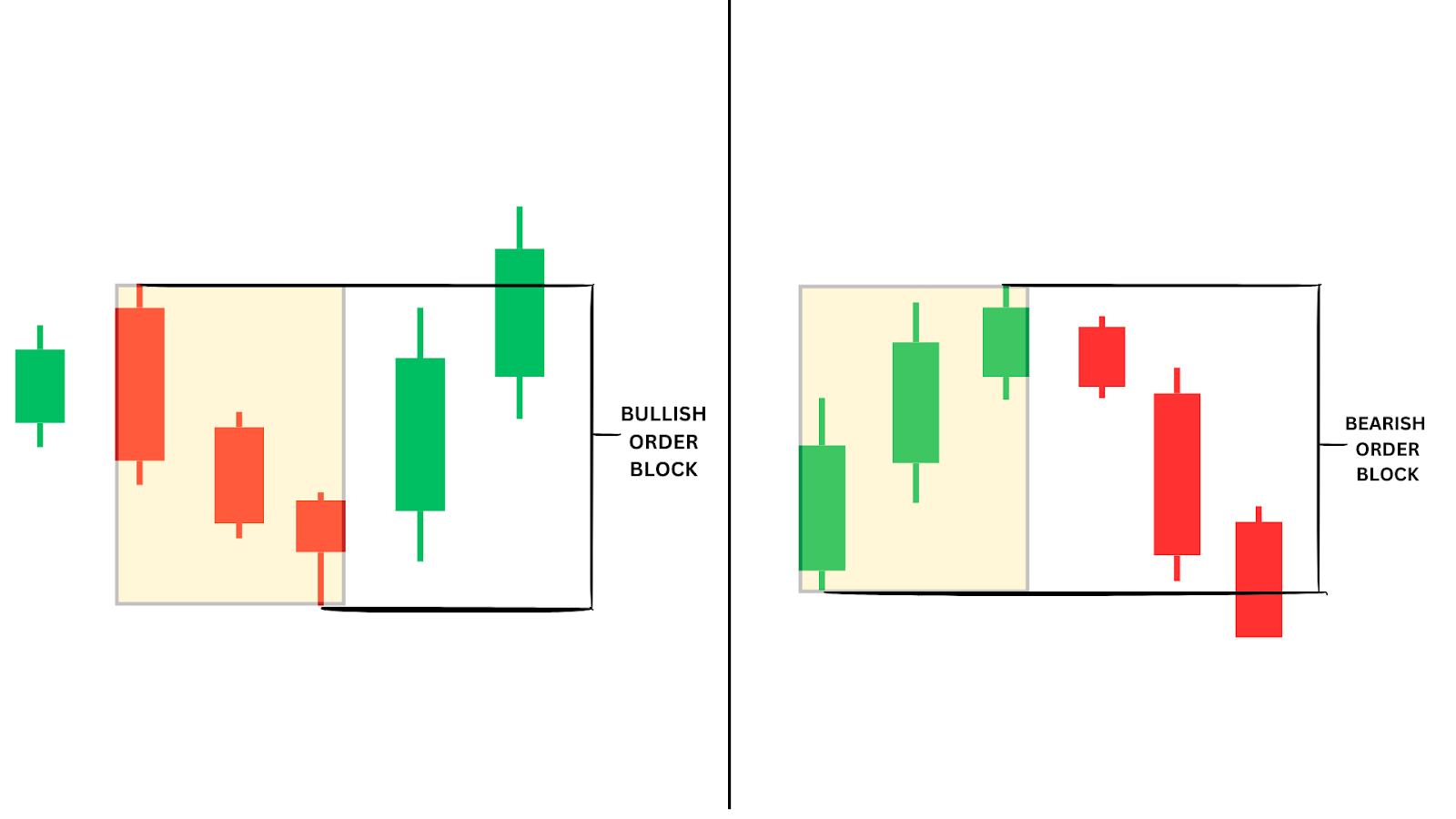
Order Blocks and FVGs are a powerful combination. Order Blocks represent areas where large institutions have placed significant buy or sell orders, creating zones of interest. FVGs within these Order Blocks act as prime entry points. The FVG provides a refined area to enter the market while the Order Block adds strength to the setup.
Change of Character (ChoCH)
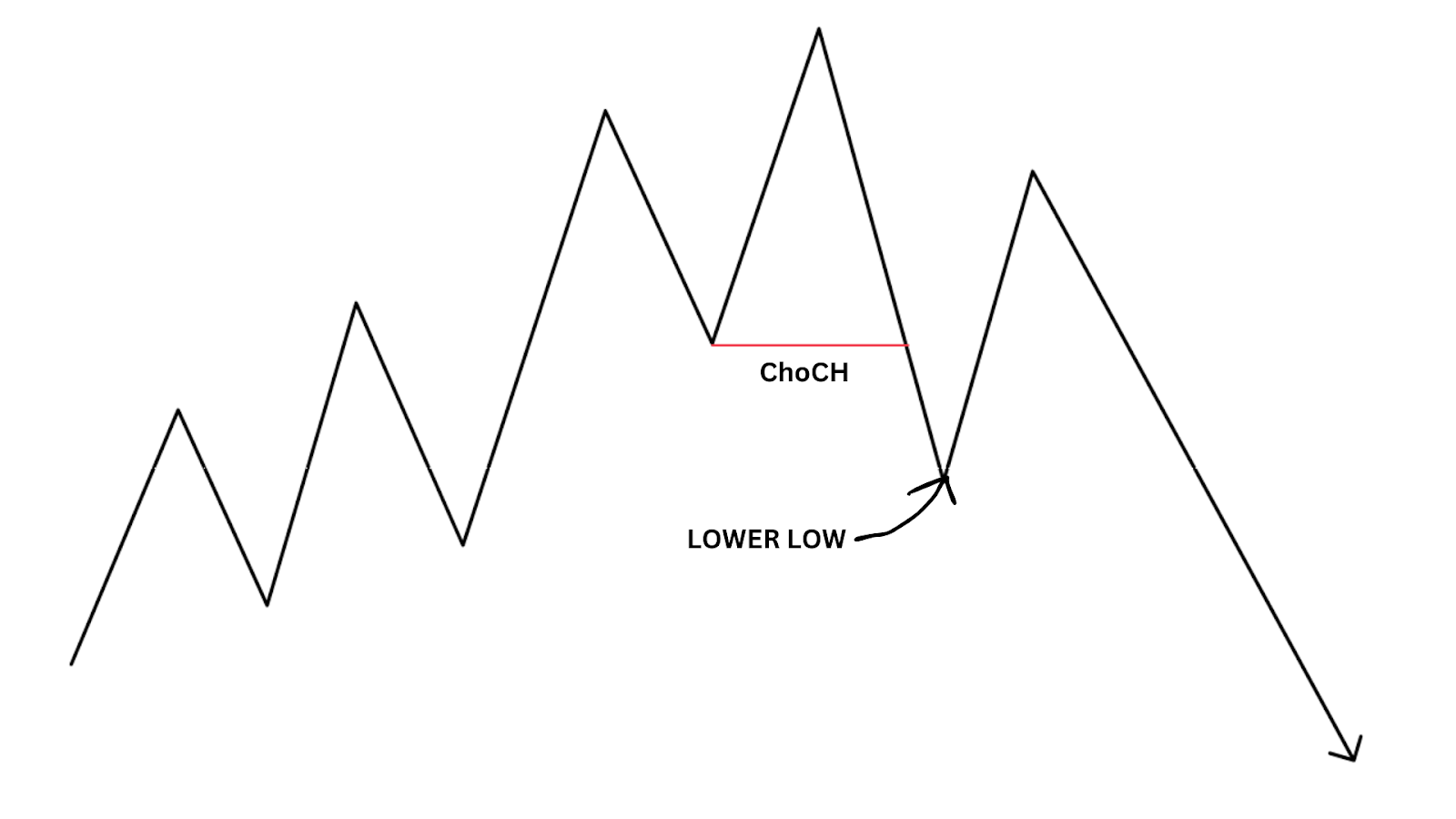
A Change of Character (ChoCH) indicates a shift in market structure, signalling the start of a new trend. When a ChoCH aligns with an FVG, it provides strong confirmation for entering the market. For instance, if a bearish ChoCH occurs and a bearish fair value gap forms, traders can look for an ideal short entry with greater confidence.
Closing Thoughts on the Fair Value Gap
The Fair Value Gap is a unique concept that can be extremely powerful when used correctly. It allows traders to identify market imbalances, potential retracement zones and use gap trading strategies to exploit these movements.
However, it’s essential to use FVGs alongside other tools like Order Blocks, ChoCH, and market structure to avoid common pitfalls. As with any trading strategy, patience and confluence are key to success.
Advantages of Trading Fair Value Gaps
- Precise Entry Points: FVGs offer highly accurate entry points by pinpointing areas of untested price action that price action traders can exploit.
- Versatility: They work across all timeframes and markets, making them useful for different trading styles.
- High Probability Setups: When combined with other Smart Money Concepts, FVGs provide a strong framework for identifying high-probability trades.
Disadvantages of Trading Fair Value Gaps
- Requires Confirmation: FVGs alone are not always reliable and need to be combined with other strategies for better accuracy.
- Can Be Invalidated Quickly: In fast-moving markets, an FVG may be invalidated if price action moves too strongly in one direction.
- Overtrading Risk: Traders may over-rely on FVGs, leading to overtrading without sufficient confluence from other indicators.
Prove. Trade. Get Funded
At FXIFY™, we believe in providing traders with the capital and tools they need to succeed.
Our challenge accounts range from $5k all the way up to $400k in trading capital once you pass the evaluation. Plus, with performance splits reaching 90% and bi-weekly payout add-ons at checkout, you’re more in control then ever when it comes to your trading.
The best part? You can request your first payout on demand after just one profitable live trade. No gimmicks, no waiting periods – just fast, reliable payouts.
FAQ Section
What does FVG mean in trading?
In trading, FVG stands for Fair Value Gap. It’s an unfilled gap in price action created when the market moves too quickly, causing no overlap between candle wicks or bodies. Traders use FVGs to identify areas where price might return to ‘fill’ the gap before resuming its trend. These gaps often signal potential future entry and exit points for traders.
How to identify bullish FVG?
A bullish FVG forms during a sharp upward movement when a gap appears between consecutive bullish candles. To spot it, look for a rapid price increase with no overlap between the low of one bullish candle and the high of the previous one. This gap may serve as a support zone where price could retrace before continuing higher, offering buy opportunities.
How to identify bearish FVG?
A bearish FVG forms during a fast downward move when there’s no overlap between the high of one bearish candle and the low of the previous one. This creates a resistance zone where the market may retest the gap before continuing its decline, providing possible short-selling opportunities.
What is the difference between fair value gap and liquidity void?
Both represent market imbalances, but an FVG occurs when rapid price movement creates a specific gap in the price structure. A liquidity void is broader and reflects a lack of market liquidity, often seen after major events. While FVGs pinpoint gaps within price moves, liquidity voids are wider areas of low liquidity, typically driven by volatility or news.
How reliable is the fair value gap?
The reliability of FVGs depends on the timeframe and confluence with other indicators. They are more dependable on higher timeframes like 4-hour or daily charts because they show institutional activity. Combining FVGs with tools like Order Blocks or Change of Character (ChoCh) improves their accuracy. On lower timeframes, they can be less reliable due to market noise.
Where does the fair value gap tend to form?
Fair Value Gaps often form after periods of high volatility or price surges, such as after news releases or major market events. They can appear around key support or resistance levels, or during trend reversals, providing clues for potential retracement points before the trend resumes.
Which indicators work best with Fair Value Gaps?
Moving averages, Fibonacci retracements, and Smart Money Concepts (SMC) like Order Blocks and Change of Character (ChoCh) complement FVGs well. Tools like Volume Profile and VWAP are also useful to confirm the strength of price movement, ensuring traders align with institutional activity.





