Among the many trading strategies available, one method prioritising planning over constant monitoring is ‘Set and Forget’ trading — a method used worldwide to simplify execution. This strategy involves setting up a trade entry, stop-loss, and profit target, and then letting the market run its course without intervention. But is this Set and Forget strategy effective for forex traders, the stock market, and broader global financial markets?
This article explores the Set and Forget approach — its core concepts, pros, cons, and how it fits different trading strategies, including prop trading. This guide helps you decide if this strategy fits your trading plan.
What is ‘Set and Forget’ Trading?
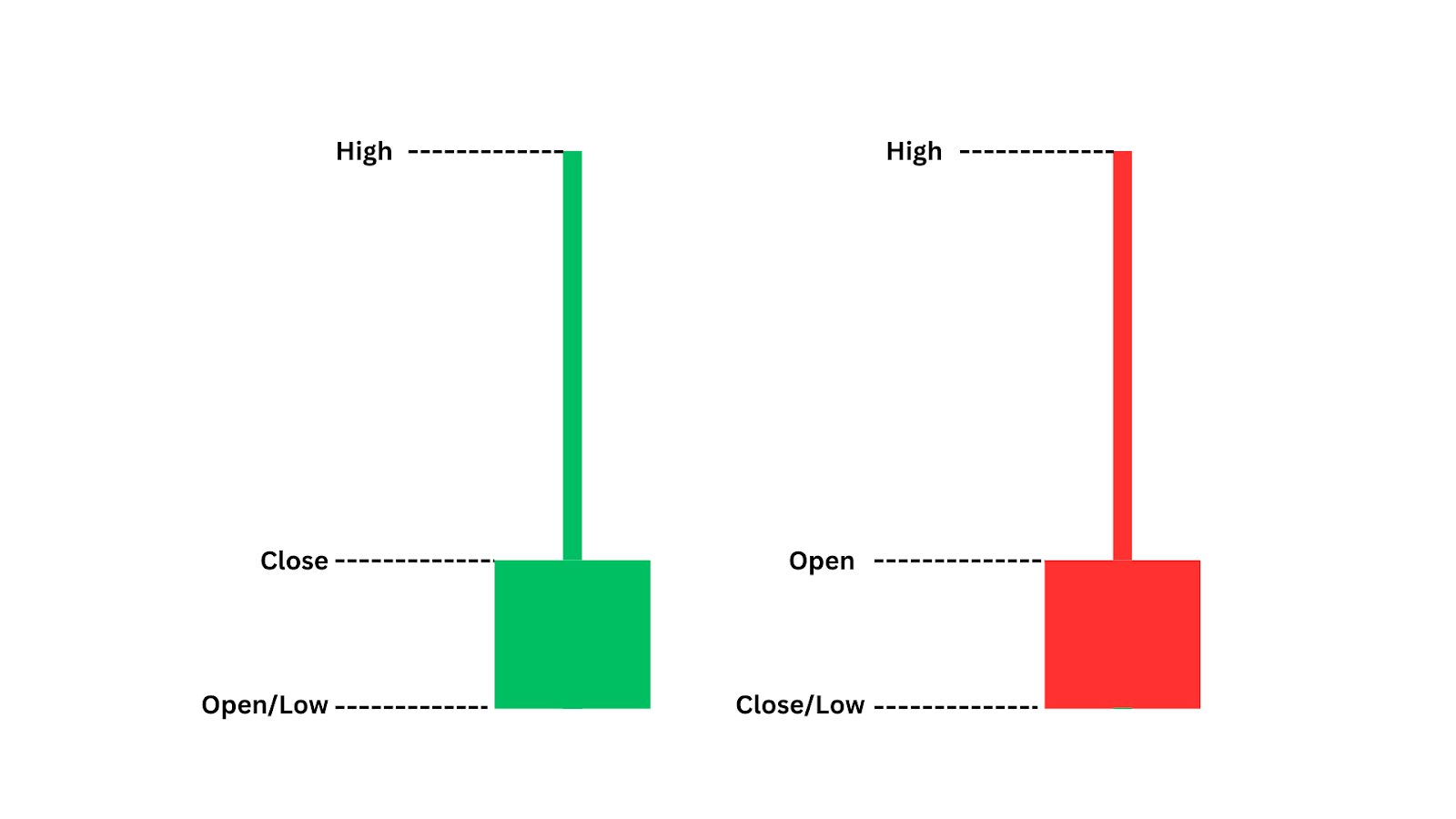
‘Set and Forget’ trading is a strategy where traders do all the analysis beforehand, and place orders with predefined entry, stop-loss, and take-profit levels. Once live, the trade runs independently.
The hallmark of this strategy is non-intervention. The trade will automatically close when either the stop-loss or take-profit target is hit. This detachment reduces emotional decisions and supports discipline and time efficiency.
This approach suits traders who want minimal trade management time and manage their stress levels. Once you set the trade, forget it and come back when it wins and loses. An important note: this approach is usually discretionary—that means entries and exits are based on a trader’s analysis, not purely algorithmic or automated systems.
Limit orders support this passive style by defining entries in advance. You establish the position, walk away, and let the market decide the outcome.
Key Principles of Set and Forget
Three core principles define the Set and Forget trading approach:
- Pre-Trade Planning: All trade parameters must be defined before execution. This includes detailed market analysis—primarily technical (support/resistance levels, trendlines, price action), and sometimes fundamental—to determine the exact entry, stop-loss (based on market structure), and a realistic take-profit target. This defines the full trade setup before execution.
- No Post-Execution Adjustment: Strict adherence is key. Once the trade is live, traders must resist the urge to adjust stop-loss or take-profit levels, regardless of market movement or emotional impulses. No reacting. No tweaking. Trust the plan.
- Emphasis on Discipline: Success depends on trusting the original trade setup, and avoiding emotional decisions during its operation. Let the setup play out without interference from fear or greed.

Why ‘Set and Forget’ Works: The Benefits
Sticking to these principles offers several advantages for this set and forget strategy:
Emotional Control
Trading psychology is one of the biggest challenges that even a professional trader may face. This technique reduces the influence of fear, greed, and impulsiveness by removing the need to manage trades mid-flight. It reduces stress and discourages overtrading.
Time Efficiency
This strategy is ideal for traders who can’t spend much time at the screens or wonder how much time they need to trade effectively. Once a trade is placed, you can walk away — allowing more time for other commitments, strategic development, or simply avoiding screen fatigue.
Enhanced Objectivity
All decisions are made in advance and based on a clear price action analysis. This does not mean reacting emotionally or impulsively when the trade moves for or against you, but rather trusting your initial setup with good risk management. This builds discipline, strengthens trust in your process, and helps you stay consistent over time.
How Set and Forget Fits Different Trading Styles
The suitability of Set and Forget varies by trading timeframe and is not ideal for all trading strategies:
| Trading Style | Suitability | Reason / Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Scalping | Low | Requires constant, rapid decisions incompatible with the passive nature of Set and Forget. This is one of the unsuitable short-term strategies. |
| Day Trading | Medium | Can work for specific setups (e.g., breakouts from key daily levels) but requires careful analysis within the day. A clear trade set with a stop loss and profit target is key. |
| Swing Trading | High | Aligns well with holding trades for days/weeks based on analysis of larger market trends (e.g., daily charts), and typically with wider stop loss. This works extremely well with the Set and Forget approach. |
| Position Trading | High | Ideal for long-term trades (weeks/months) based on major market trends, where infrequent adjustments and focus on key levels match the Set and Forget ethos. |
Practical Applications and Setups
Several technical strategies work naturally with a Set and Forget approach, especially those that rely on clean, rule-based setups rooted in price action.
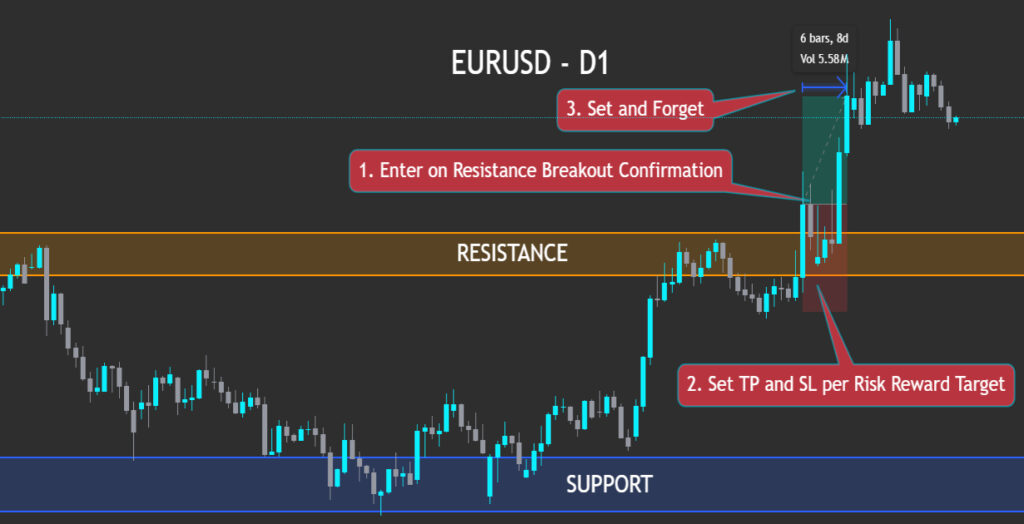
Breakout Trades
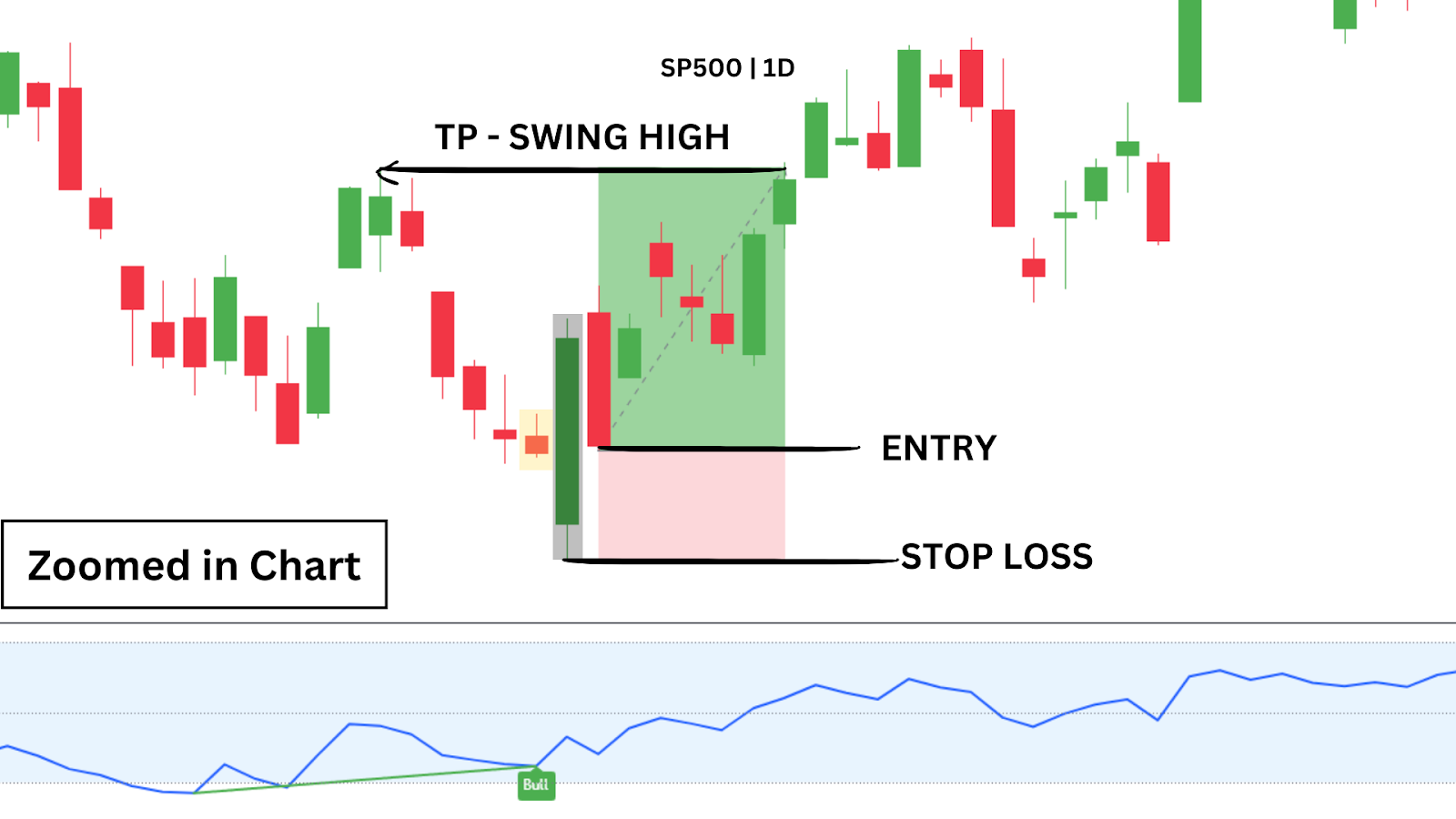
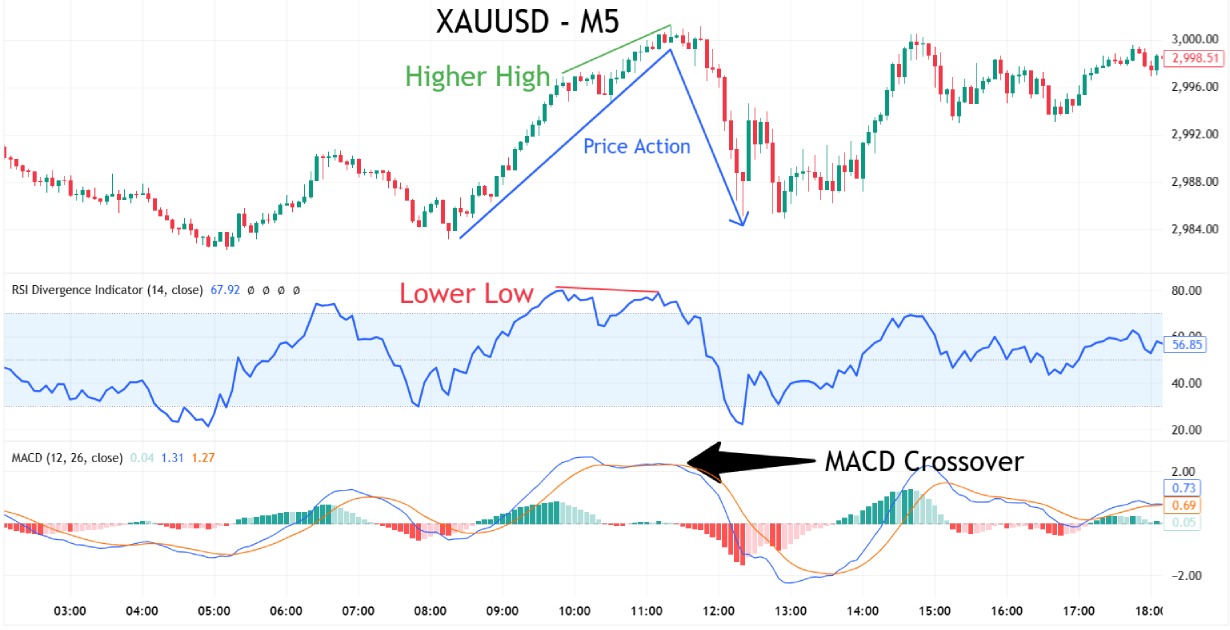
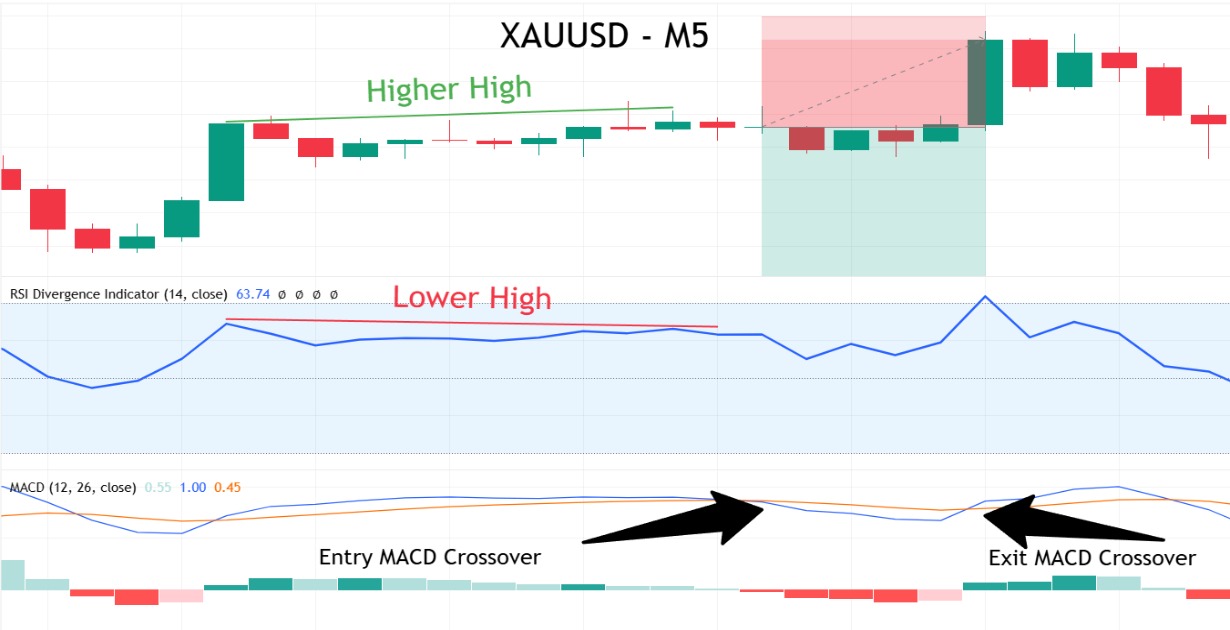
Look for a clear support or resistance level on the chart. Place a buy stop (or sell stop) just beyond the breakout level, a stop-loss on the opposite side, and a take-profit based on a measured move or prior market structure. Once live, step back and let the trade run.
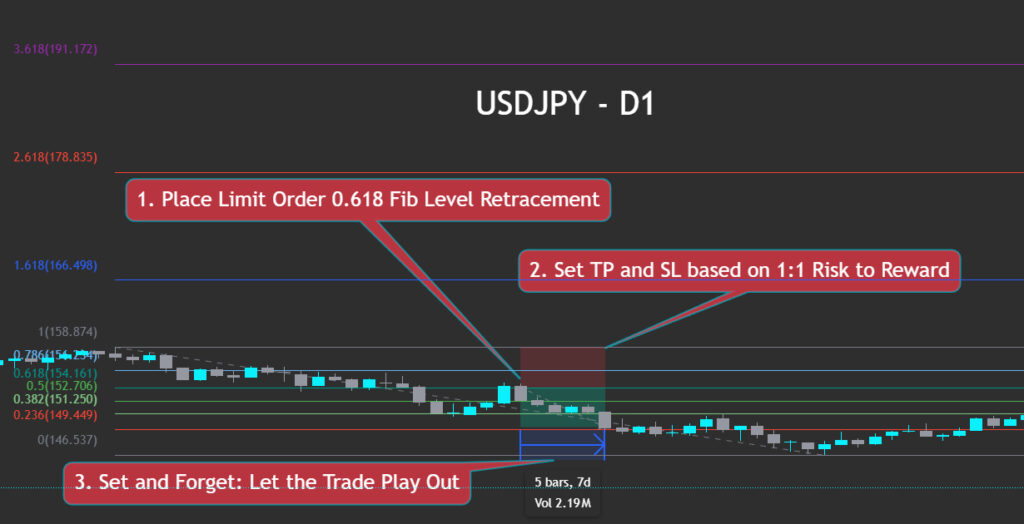
Fibonacci Retracements
Consider using Fibonacci levels or moving averages to identify likely pullback zones. Enter using a limit order, place your stop-loss beyond the previous swing, and set a target in the direction of the trend.
After entry, avoid adjusting — trust the setup to unfold.
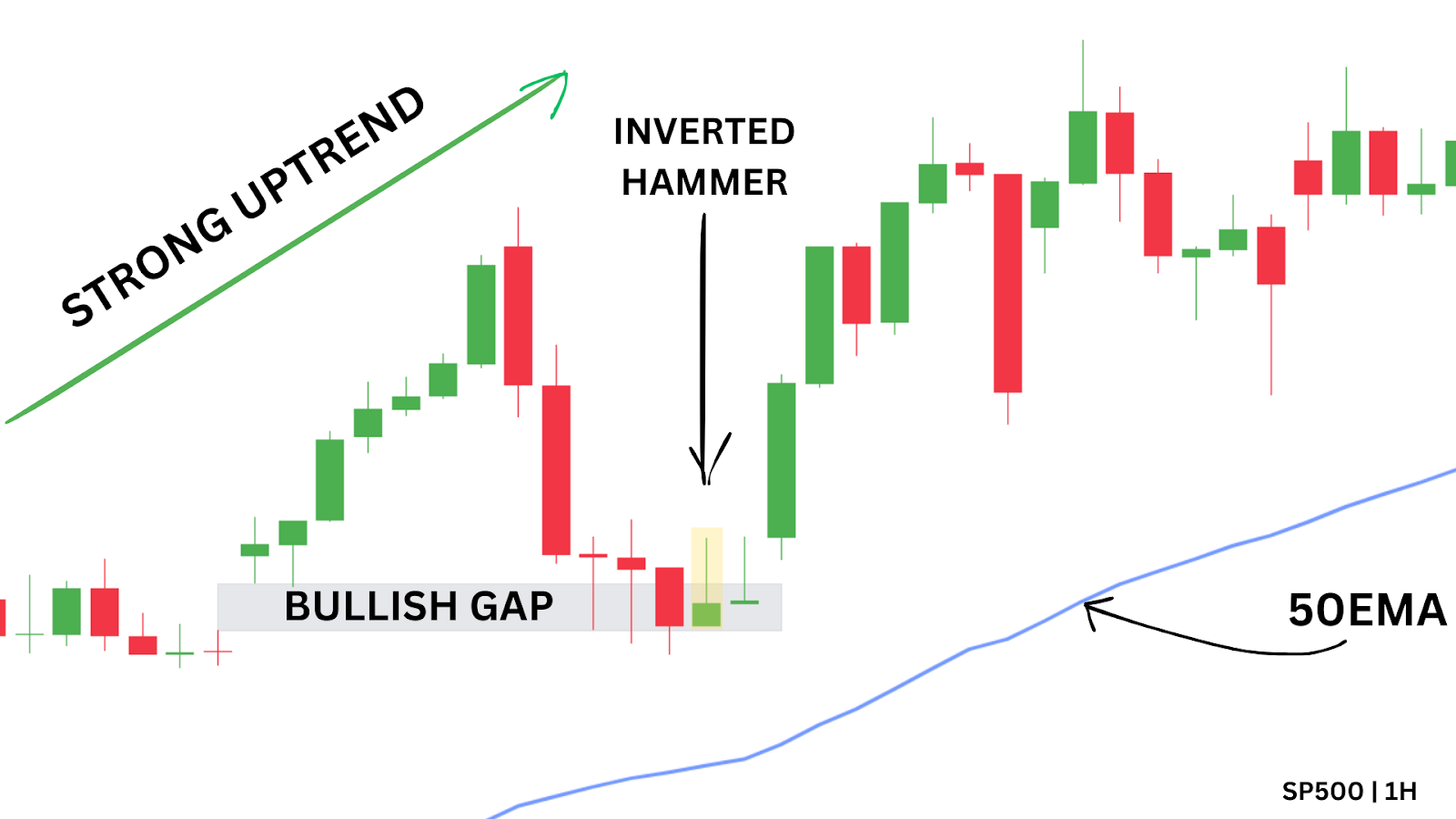
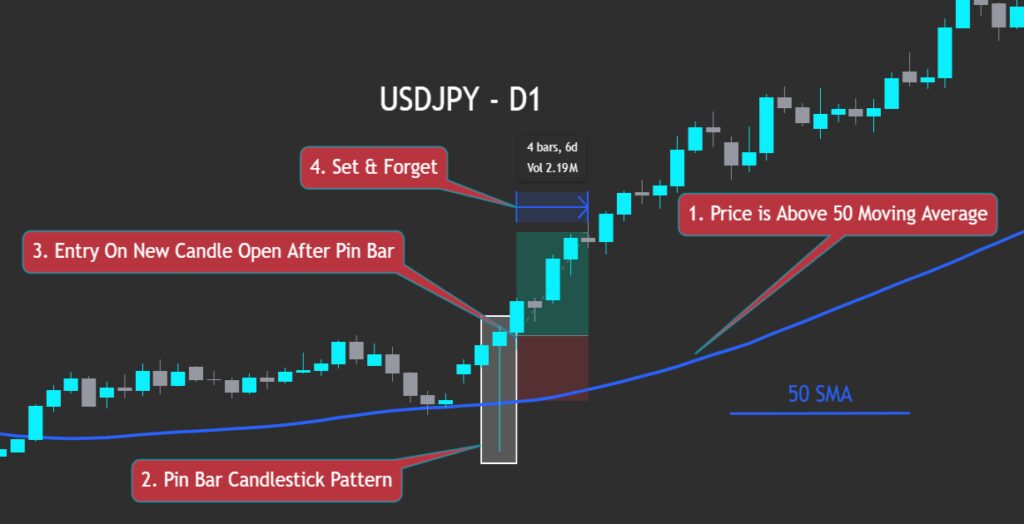
Trend-Following with Price Action
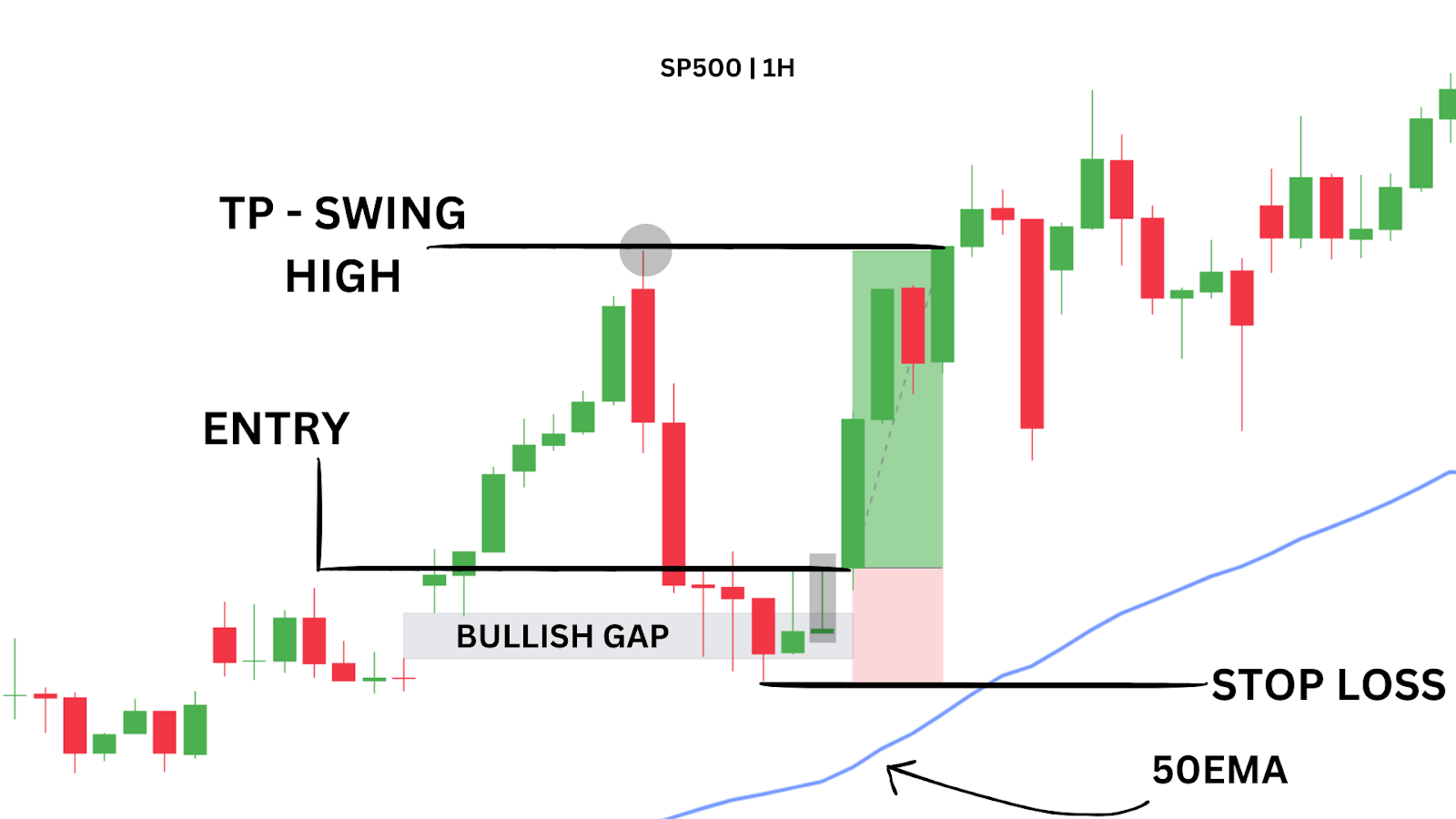
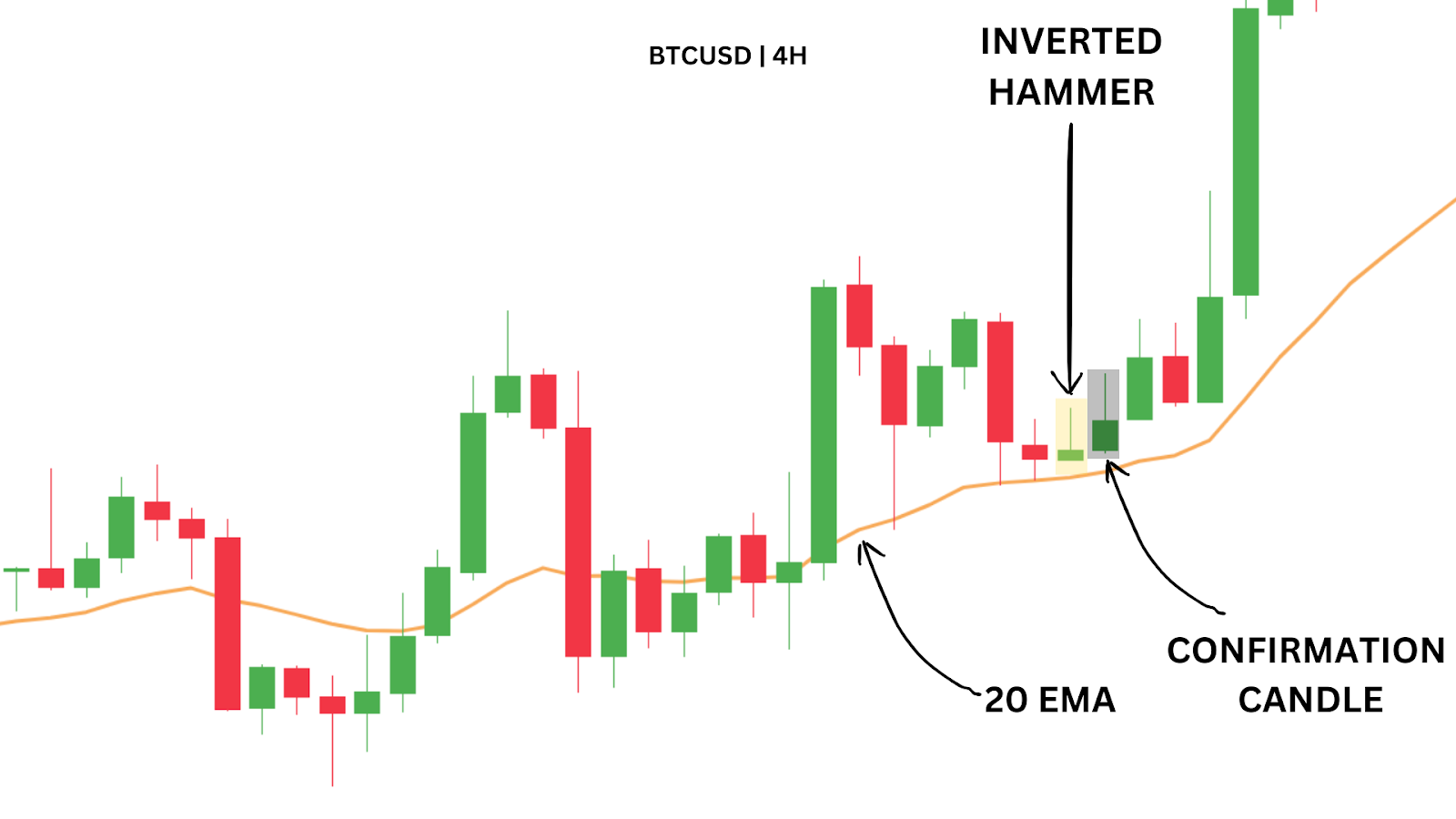
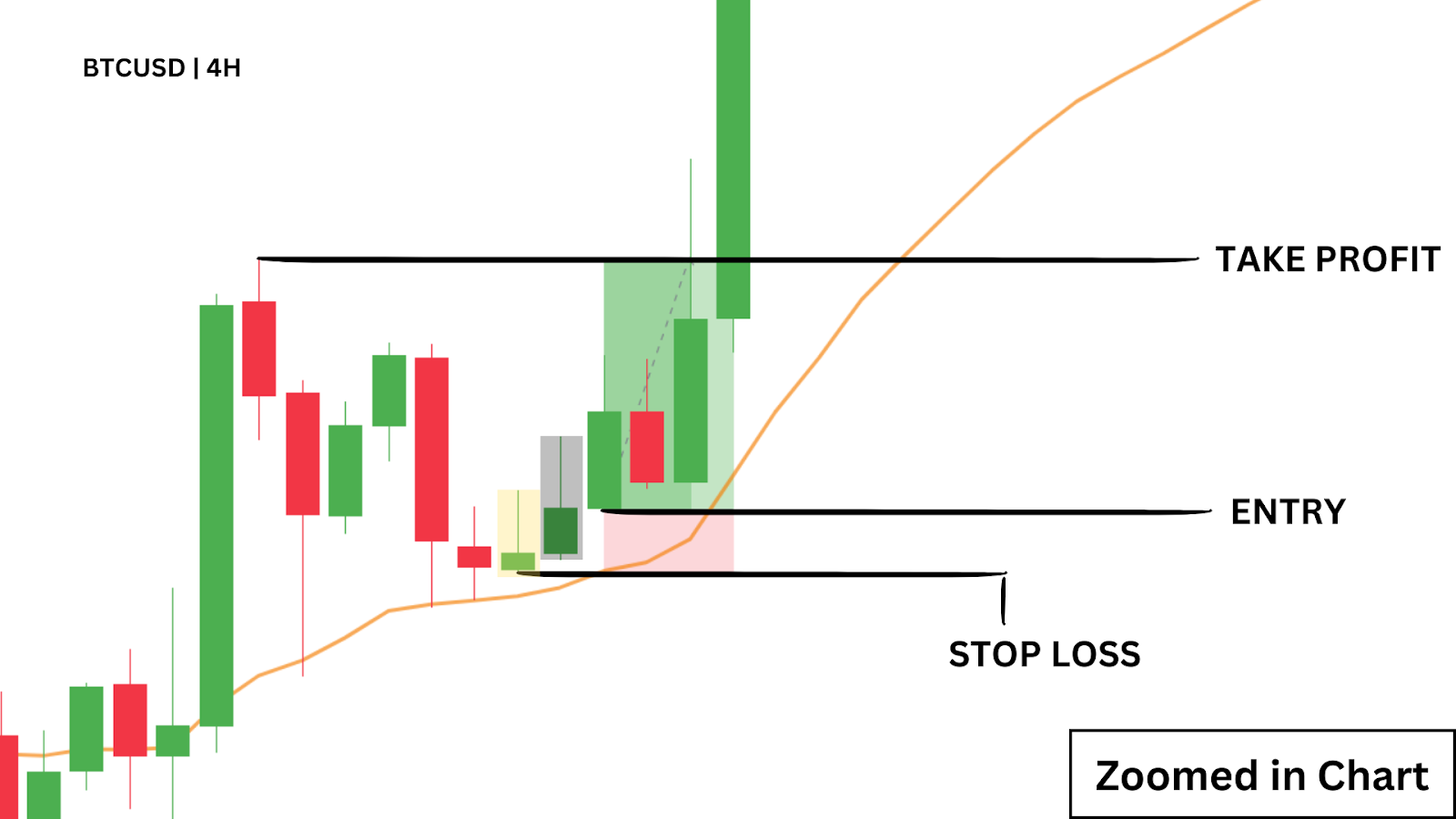
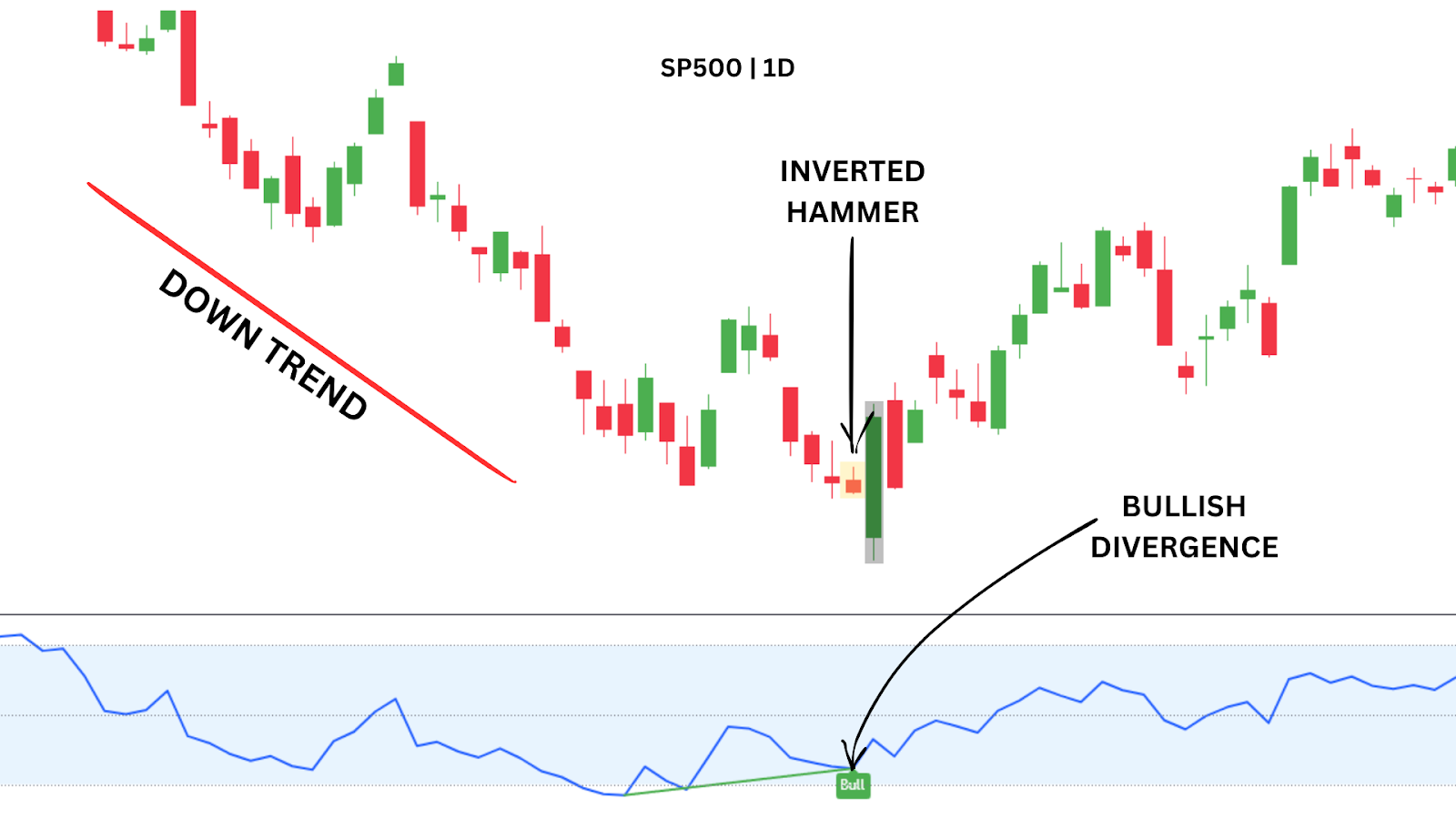
In a clear up‑trend—price above the 50 SMA—you might wait for a bullish pin‑bar or engulfing candle as a continuation signal. Buy on the next candle’s open, set your stop‑loss just below the 50 SMA, and define your take‑profit per your risk/reward plan. Then “set and forget”—let the trade run without mid‑trade edits.
Building Risk Control into Your ‘Set and Forget’ Trade
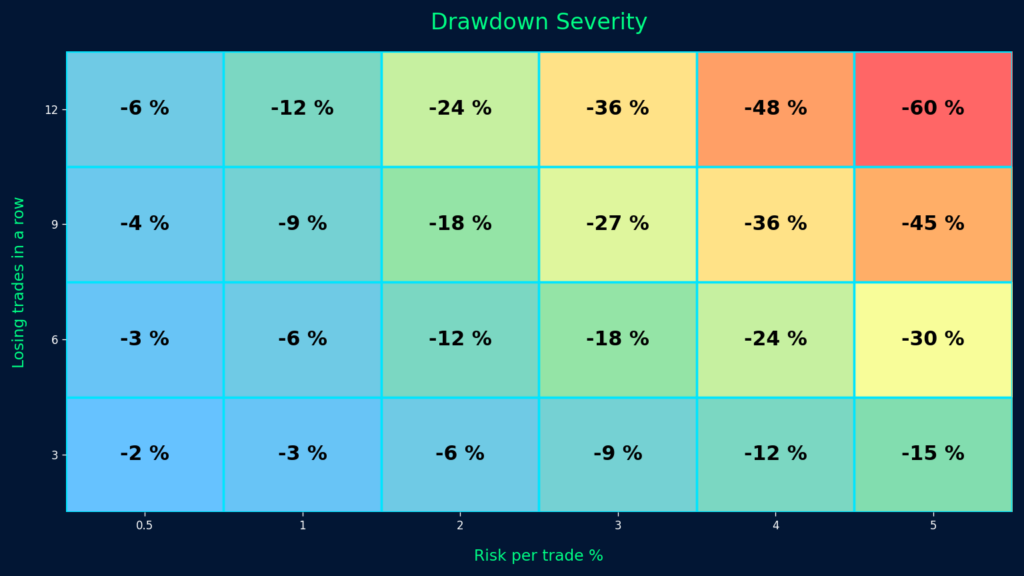
Effective risk management is critical in Set and Forget trading, especially since you’re not monitoring trades in real-time. Every decision must be precise and pre-planned.
Stop-Loss and Take-Profit Placement
Your stop-loss and take-profit levels should be based on sound technical analysis — such as market structure, recent volatility, or key price zones. Avoid placing them based on emotion or arbitrary profit targets that ignore market conditions. Poorly placed exits can cause premature trade closures, large drawdowns, or even risk triggering a margin call in fast-moving conditions. Rule-based exits are essential.
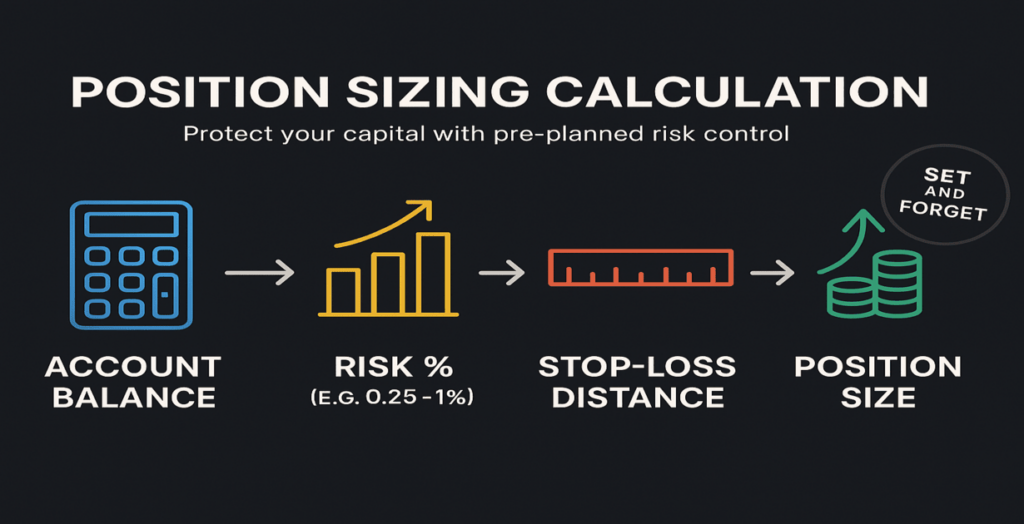
Position Sizing
Before placing a trade, calculate your position size to ensure the potential loss is only a small percentage of your equity, helping maintain long-term capital preservation.
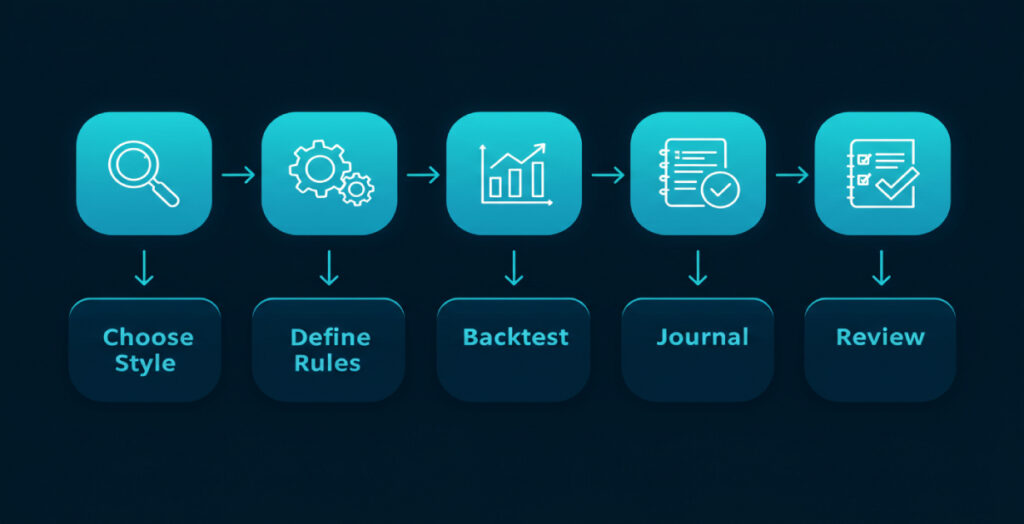
Backtesting
Always backtest your strategy before going live. This allows you to see how successful your strategy is across different market conditions and trading strategies. Set and Forget relies on trusting the plan — and that trust is built through data.
Market Suitability
Set and Forget works best in clean, trending environments — especially in the forex market, where structure and momentum can support clear setups.
It’s less effective in highly volatile, low-liquidity, or news-driven environments where sudden spikes or gaps can trigger stops unexpectedly. Always assess the trading environment before applying the strategy… adaptability matters just as much as discipline.
Limitations of Set and Forget Trading
While Set and Forget offers structure and discipline, it’s important to understand where it can fall short.
Rigidity
This strategy cannot adapt to real-time market developments. If major news or volatility hits after the trade is placed, the trade continues as planned, even if conditions have changed dramatically. This lack of flexibility is one of its key risks, especially in volatile stock or forex markets.
Missed Opportunities
A fixed take-profit like 1:2 RR means you might exit the trade while the move continues to trend higher. Additionally, if the market reverses just before reaching the take-profit, unrealised gains can disappear entirely. There’s no room to react once the trade is active.
All-or-Nothing Outcomes
Set and Forget trades usually reach either the stop-loss or the full target. Without options like scaling out or trailing stops, large potential gains can turn into full losses. The predefined setup controls the result — for better or worse.
Market Dependence
It performs best in directional markets. In choppy or low-volume conditions, small losses are common. Set and Forget requires the right market context to work effectively.
Optimising the Set and Forget Approach
While Set and Forget prioritises simplicity, you can enhance it without sacrificing core principles. Consider these predefined refinements to boost performance and flexibility:
- Flexible Rules (Pre-Planned):
Establish dynamic management rules in advance, such as moving the stop-loss to breakeven after a certain risk-to-reward milestone (e.g., 1:1). This remains within the Set and Forget mindset.
- Trailing Stop-Loss:
Define a trailing stop before trade execution. It automatically adjusts in your favour, locking in profits while capturing larger moves without manual intervention.
- Multiple Targets:
Plan exits at several predefined levels. For instance, close half the trade at the first target, adjust stop-loss to breakeven and then let the remainder run to the next target.
- Contextual Analysis:
Enhance entry accuracy using top-down analysis—from higher timeframes for broader trends to lower timeframes for precise entries—while preserving hands-off execution.
- Trade Alerts:
Set up automated alerts that notify you as the price approaches key levels. This eliminates constant chart monitoring, aligning perfectly with the Set and Forget approach.
Set and Forget in Prop Trading
Prop firm challenges and funded accounts require strict adherence to predefined rules. Here’s how Set and Forget fits into that environment:
Master Market Level Identification:
Identify precise price levels for entries, stops, and take-profits. These must align with the structure, profit targets, and drawdown limits.
Plan Risk in Advance:
Calculate position size so a loss stays within firm drawdown limits. Avoid relying on manual intervention.
Use a Backtested Strategy with Edge:
Set and Forget only works in prop trading if it’s a proven, profitable strategy. Backtest rigorously to confirm your risk/reward aligns with firm rules and timelines.
Monitor Performance and Rule Compliance:
Track metrics like win rate and average risk-to-reward over time. Confirm that your strategy not only meets your trading edge but also complies with the firm’s rules at every stage — from challenge to funded account.
Trading During Economic News:
In a Nutshell…
Set and Forget trading is a structured approach that balances strategic planning with psychological discipline. Defining trade parameters before execution — including entry, stop-loss, and take-profit — and avoiding mid-trade adjustments, help reduce emotional errors and support time efficiency. For many forex traders, this simplicity and hands-off nature are highly appealing for taking advantage of structured trade setups.
That said, it’s not a universal solution. This method may not suit all traders, especially forex traders using reactive, high-frequency strategies, or market conditions, particularly in choppy or highly reactive environments. But in structured or trending markets — especially swing or position trading — it works well.
Its strengths lie in removing emotional interference, managing time constraints, and encouraging objective, rule-based execution. However, success depends on several key factors: trading skills, strong market analysis, well-calculated position sizing, disciplined risk management, and consistent review of trade outcomes.
When applied carefully, it supports a sustainable, logic-based trading process.